'High dose' vs. 'medium dose' UVA1 phototherapy in italian patients with severe atopic dermatitis
- PMID: 30468530
- PMCID: PMC6440836
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.15362
'High dose' vs. 'medium dose' UVA1 phototherapy in italian patients with severe atopic dermatitis
Abstract
Background: The current evidences attest UVA1 phototherapy as effective in the treatment of severe atopic dermatitis (AD). Furthermore, in this indication, 'medium dose' is as effective as 'high dose' regimen. To date, a randomized comparison study evaluating the effectiveness as well as safety of different UVA1 protocols in different skin types in the treatment of adult patients with severe AD is still lacking.
Objective: The aim of the present study was to compare the safety and the efficacy of medium and high dose UVA1 either in fair or in dark skin types.
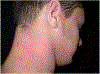
Methods: Twenty-seven adult patients with severe AD were consecutively included in a randomized, controlled, open, two arms trial Severity of AD was determined by means of SCORAD index and clinical improvement was also monitored. A total of 13 out of 27 patients were treated with high dose (130 J/cm2 ) UVA1 protocol while 14 out of 27 patients received medium dose (60 J/cm2 ) UVA1 protocol. Phototherapy was performed five times weekly up to 3 weeks. Before and after UVA1 treatment each patient was evaluated for skin pigmentation through Melanin Index (MI) quantitative evaluation.
Results: Skin status improved in all patients resulting in a reduction of SCORAD index in all groups. Our results demonstrated that among patients with darker skin types and higher MI, high dose UVA1 was significantly more effective than medium dose (P < 0.0001) while within the groups with skin type II, no significant differences between high and medium dose protocols were observed.
Conclusion: Our study, confirms previous observations that UVA1 phototherapy should be considered among the first approaches in the treatment of patients with severe generalized AD and also demonstrates that in darker skin types, high dose UVA1 phototherapy is more effective than medium dose in the treatment of adult patients with severe AD.
© 2018 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures





References
-
- Abramovits W Atopic Dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 53: S86–93 - PubMed
-
- Karsen FS, Hanifin JM. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Allergy Clin North Am 2002; 22: 1–24
-
- Larse FS, Holm NV, Henningsen K. Atopic dermatitis. A genetic-epidemiologic study in a population based twin sample. J Am Acad Dermatol 1986; 15: 487–94 - PubMed
-
- Asadullah K, Sterry W, Trefzer U. Cytokines: interleukin and interferon therapy in dermatology. Clin Exp Dermatol 2002; 27: 578–84 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

