Imaging and Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review
- PMID: 30469491
- PMCID: PMC6321449
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19123702
Imaging and Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review
Abstract
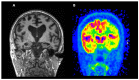
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and is a significant burden for affected patients, carers, and health systems. Great advances have been made in understanding its pathophysiology, to a point that we are moving from a purely clinical diagnosis to a biological one based on the use of biomarkers. Among those, imaging biomarkers are invaluable in Alzheimer's, as they provide an in vivo window to the pathological processes occurring in Alzheimer's brain. While some imaging techniques are still under evaluation in the research setting, some have reached widespread clinical use. In this review, we provide an overview of the most commonly used imaging biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease, from molecular PET imaging to structural MRI, emphasising the concept that multimodal imaging would likely prove to be the optimal tool in the future of Alzheimer's research and clinical practice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); positron emission tomography (PET).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Prince M., Wimo A., Guerchet M., Ali G., Wu Y., Prina M. World Alzheimer Report 2015—The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI); London, UK: 2015.
-
- McKhann G.M., Knopman D.S., Chertkow H., Hyman B.T., Jack C.R., Jr., Kawas C.H., Klunk W.E., Koroshetz W.J., Manly J.J., Mayeux R., et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

