Dyspnea on exertion provokes unpleasantness and negative emotions in women with obesity
- PMID: 30471435
- PMCID: PMC6326838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2018.11.008
Dyspnea on exertion provokes unpleasantness and negative emotions in women with obesity
Abstract
Purpose: While dyspnea on exertion (DOE) is a common complaint in otherwise healthy obese women, less is known about feelings of unpleasantness and/or negative emotions provoked by DOE. We examined whether ratings of perceived breathlessness (RPB) during exercise were associated with ratings of unpleasantness and negative emotions (depression, anxiety, frustration, anger, and fear) in obese women.
Methods: Seventy-four women (34 ± 7 yrs, 36 ± 4 kg/m2, 46 ± 5% body fat) performed 6 min of constant-load cycling (60 W); RPB (0-10 scale), and unpleasantness and negative emotions (visual analog scales, 10 cm) were assessed at the end.
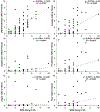
Results: RPB were significantly correlated with unpleasantness and negative emotions (p < 0.05). The strongest correlations were between RPB and unpleasantness (r = 0.61, p < 0.001), and RPB and anxiety (r = 0.50, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: DOE can significantly provoke unpleasantness and negative emotions during exercise in obese women. This may affect their willingness to engage in regular physical activity.
Keywords: Affective dimension; Exertional breathlessness; Obesity; Physical activity; Respiratory symptoms.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
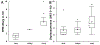
References
-
- 1994. Plan and operation of the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–94. Series 1: programs and collection procedures. Vital Health Stat 1, 1–407. - PubMed
-
- Babb TG, DeLorey DS, Wyrick BL, Gardner PP, 2002. Mild obesity does not limit change in end-expiratory lung volume during cycling in young women. Journal of applied physiology 92, 2483–2490. - PubMed
-
- Babb TG, Ranasinghe KG, Comeau LA, Semon TL, Schwartz B, 2008a. Dyspnea on exertion in obese women: association with an increased oxygen cost of breathing. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 178, 116–123. - PubMed
-
- Babb TG, Wyrick BL, DeLorey DS, Chase PJ, Feng MY, 2008b. Fat distribution and end-expiratory lung volume in lean and obese men and women. Chest 134, 704–711. - PubMed
-
- Banzett RB, Dempsey JA, O’Donnell DE, Wamboldt MZ, 2000. Symptom perception and respiratory sensation in asthma. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 162, 1178–1182. - PubMed

