rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 in Preterm Infants: A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30471715
- PMCID: PMC6389415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.10.033
rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 in Preterm Infants: A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: To investigate recombinant human insulin-like growth factor 1 complexed with its binding protein (rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3) for the prevention of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and other complications of prematurity among extremely preterm infants.
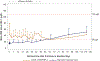
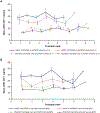
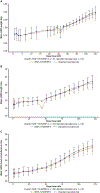
Study design: This phase 2 trial was conducted from September 2014 to March 2016. Infants born at a gestational age of 230/7 weeks to 276/7 weeks were randomly allocated to rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 (250 µg/kg/ 24 hours, continuous intravenous infusion from <24 hours of birth to postmenstrual age 296/7 weeks) or standard neonatal care, with follow-up to a postmenstrual age of 404/7 weeks. Target exposure was ≥70% IGF-1 measurements within 28-109 µg/L and ≥70% intended therapy duration. The primary endpoint was maximum severity of ROP. Secondary endpoints included time to discharge from neonatal care, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, intraventricular hemorrhage, and growth measures.
Results: Overall, 61 infants were allocated to rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3, 60 to standard care (full analysis set); 24 of 61 treated infants achieved target exposure (evaluable set). rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 did not decrease ROP severity or ROP occurrence. There was, however, a 53% decrease in severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in the full analysis set (21.3% treated vs 44.9% standard care), and an 89% decrease in the evaluable set (4.8% vs 44.9%; P = .04 and P = .02, respectively) for severity distribution between groups. There was also a nonsignificant trend toward decrease in grades 3-4 intraventricular hemorrhage in the full analysis set (13.1% vs 23.3%) and in the evaluable set (8.3% vs 23.3%). Fatal serious adverse events were reported in 19.7% of treated infants (12/61) and 11.7% of control infants (7/60). No effect was observed on time to discharge from neonatal care/growth measures.
Conclusions: rhIGF-1/rhIGFBP-3 did not affect development of ROP, but decreased the occurrence of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia, with a nonsignificant decrease in grades 3-4 intraventricular hemorrhage.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01096784.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; intraventricular hemorrhage; neonatology; retinopathy of prematurity.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Langford K, Nicolaides K, Miell JP. Maternal and fetal insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the second and third trimesters of human pregnancy. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1389–93. - PubMed
-
- Hansen-Pupp I, Löfqvist C, Polberger S, Niklasson A, Fellman V, Hellstrom A, et al. Influence of insulin-like growth factor I and nutrition during phases of postnatal growth in very preterm infants. Pediatr Res 2011;69:448–53. - PubMed
-
- Lineham JD, Smith RM, Dahlenburg GW, King RA, Haslam RR, Stuart MC, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor I levels in newborn premature and full-term infants followed longitudinally. Early Hum Dev 1986;13:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Hellström A, Engstrom E, Hård AL, Albertsson-Wikland K, Carlsson B, Niklasson A, et al. Postnatal serum insulin-like growth factor I deficiency is associated with retinopathy of prematurity and other complications of premature birth. Pediatrics 2003; 112:1016–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

