MYC Induces a Hybrid Energetics Program Early in Cell Reprogramming
- PMID: 30472011
- PMCID: PMC6294174
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.10.018
MYC Induces a Hybrid Energetics Program Early in Cell Reprogramming
Abstract
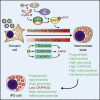
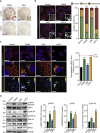
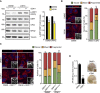
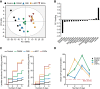
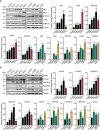
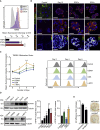
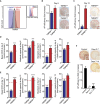
Cell reprogramming is thought to be associated with a full metabolic switch from an oxidative- to a glycolytic-based metabolism. However, neither the dynamics nor the factors controlling this metabolic switch are fully understood. By using cellular, biochemical, protein array, metabolomic, and respirometry analyses, we found that c-MYC establishes a robust bivalent energetics program early in cell reprogramming. Cells prone to undergo reprogramming exhibit high mitochondrial membrane potential and display a hybrid metabolism. We conclude that MYC proteins orchestrate a rewiring of somatic cell metabolism early in cell reprogramming, whereby somatic cells acquire the phenotypic plasticity necessary for their transition to pluripotency in response to either intrinsic or external cues.
Keywords: cell reprogramming; cell signaling; metabolism; mitochondrial dynamics.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early ERK1/2 activation promotes DRP1-dependent mitochondrial fission necessary for cell reprogramming.Nat Commun. 2016 Mar 31;7:11124. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11124. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27030341 Free PMC article.
-
c-MYC Triggers Lipid Remodelling During Early Somatic Cell Reprogramming to Pluripotency.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Dec;17(6):2245-2261. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10239-2. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 34476741 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear reprogramming with c-Myc potentiates glycolytic capacity of derived induced pluripotent stem cells.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013 Feb;6(1):10-21. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9431-2. Epub 2012 Dec 18. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23247633 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dynamics and Cristae Shape Changes During Metabolic Reprogramming.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Oct;39(10-12):684-707. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0268. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 37212238 Review.
-
Mitophagy-driven metabolic switch reprograms stem cell fate.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(1):27-43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2922-9. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30267101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial metabolism in neural stem cells and implications for neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 4;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05041-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38438847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic metabolic reprogramming in dendritic cells: An early response to influenza infection that is essential for effector function.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Oct 26;16(10):e1008957. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008957. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33104753 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of the Metabolic Shift during Somatic Cell Reprogramming.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 7;20(9):2254. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092254. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31067778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics in cancer stem cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Apr;78(8):3803-3816. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03773-2. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33580834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic control of induced pluripotency.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 11;11:1328522. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1328522. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38274274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abad M., Mosteiro L., Pantoja C., Cañamero M., Rayon T., Ors I., Graña O., Megías D., Domínguez O., Martínez D. Reprogramming in vivo produces teratomas and iPS cells with totipotency features. Nature. 2013;502:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Bretones G., Delgado M.D., León J. MYC and cell cycle control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015;1849:506–516. - PubMed

