IKZF2 Drives Leukemia Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Inhibits Myeloid Differentiation
- PMID: 30472158
- PMCID: PMC6602096
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.016
IKZF2 Drives Leukemia Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Inhibits Myeloid Differentiation
Abstract
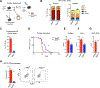
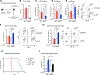
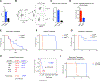
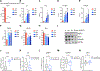
Leukemias exhibit a dysregulated developmental program mediated through both genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Although IKZF2 is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), we found that it is dispensable for mouse and human HSC function. In contrast to its role as a tumor suppressor in hypodiploid B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia, we found that IKZF2 is required for myeloid leukemia. IKZF2 is highly expressed in leukemic stem cells (LSCs), and its deficiency results in defective LSC function. IKZF2 depletion in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells reduced colony formation, increased differentiation and apoptosis, and delayed leukemogenesis. Gene expression, chromatin accessibility, and direct IKZF2 binding in MLL-AF9 LSCs demonstrate that IKZF2 regulates a HOXA9 self-renewal gene expression program and inhibits a C/EBP-driven differentiation program. Ectopic HOXA9 expression and CEBPE depletion rescued the effects of IKZF2 depletion. Thus, our study shows that IKZF2 regulates the AML LSC program and provides a rationale to therapeutically target IKZF2 in myeloid leukemia.
Keywords: C/EBP; HOXA9; IKZF2; leukemic stem cells.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
S.A.A. consults for Epizyme Inc, Imago Biosciences, Cyteir Therapeutics, C4 Therapeutics, Syros Pharmaceuticals and Accent Therapeutics. S.A.A. receives research support from Janssen, Novartis, and AstraZeneca.
Figures


Comment in
-
The Making of a Leukemic Stem Cell: A Novel Role for IKZF2 in AML Stemness and Differentiation.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Jan 3;24(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.12.007. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 30609399
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

