National Registry Data from Korean Neonatal Network: Two-Year Outcomes of Korean Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born in 2013-2014
- PMID: 30473651
- PMCID: PMC6249169
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e309
National Registry Data from Korean Neonatal Network: Two-Year Outcomes of Korean Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born in 2013-2014
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to observe long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born between 2013 and 2014 in Korea, especially focusing on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Methods: The data were collected from Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) registry from 43 and 54 participating units in 2013 and 2014, respectively. A standardized electronic case report form containing 30 items related to long-term follow up was used after data validation.
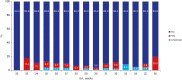
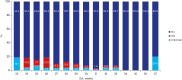
Results: Of 2,660 VLBWI, the mean gestational age and birth weight were 291/7 ± 26/7 weeks and 1,093 ± 268 g in 2013 and 292/7 ± 26/7 weeks and 1,125 ± 261 g in 2014, respectively. The post-discharge mortality rate was 1.2%-1.5%. Weight < 50th percentile was 46.5% in 2013 and 66.1% in 2014. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy among the follow up infants was 6.2% in 2013 and 6.6% in 2014. The Bayley Scales of Infant Developmental Outcomes version II showed 14%-25% of infants had developmental delay and 3%-8% of infants in Bayley version III. For the Korean developmental screening test for infants and children, the area "Further evaluation needed" was 5%-12%. Blindness in both eyes was reported to be 0.2%-0.3%. For hearing impairment, 0.8%-1.9% showed bilateral hearing loss. Almost 50% were readmitted to hospital with respiratory illness as a leading cause.
Conclusion: The overall prevalence of long-term outcomes was not largely different among the VLBWI born between 2013 and 2014. This study is the first large national data study of long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Cerebral Palsy; Incidence; Neurodevelopmental Outcome; Very Low Birth Weight Infants.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Two Year's Long-term Outcomes of Very Low Birth Weight Infants in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2018 Oct 25;33(48):e294. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e294. eCollection 2018 Nov 26. J Korean Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30473647 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cerebral Palsy Rate of Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born at 36 Weeks of Gestation.J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Mar 5;34(10):e77. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e77. eCollection 2019 Mar 18. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30886548 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Outcomes at 18-24 Months of Infants with Birth Weight under 500 g Born in Korea during 2013-2017: A Nationwide Cohort Study.Neonatology. 2024;121(1):74-80. doi: 10.1159/000534194. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Neonatology. 2024. PMID: 37866355
-
Serial Long-Term Growth and Neurodevelopment of Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants: 2022 Update on the Korean Neonatal Network.J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Aug 29;37(34):e263. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e263. J Korean Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36038959 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental outcome of very low birth weight infants in a developing country.BMC Pediatr. 2012 Feb 1;12:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-11. BMC Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 22296705 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative review of mortality and developmental disability in extremely premature newborns.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998 May;152(5):425-35. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.152.5.425. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998. PMID: 9605024 Review.
-
Improvement in the Survival Rates of Very Low Birth Weight Infants after the Establishment of the Korean Neonatal Network: Comparison between the 2000s and 2010s.J Korean Med Sci. 2017 Aug;32(8):1228-1234. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.8.1228. J Korean Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28665056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive Outcomes of Children with Very Low Birth Weight at 3 to 5 Years of Age.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Jan 6;35(1):e4. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e4. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31898433 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence of long-term neurodevelopmental impairment following extremely preterm birth: a systematic literature review.J Int Med Res. 2021 Jul;49(7):3000605211028026. doi: 10.1177/03000605211028026. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34284680 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolytic (Thrombolytic) Therapy for Post Intraventricular Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Preterm Infants.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2023 May;66(3):263-273. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2022.0258. Epub 2023 Jan 16. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2023. PMID: 36642948 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Palsy Rate of Very Low Birth Weight Infants Born at 36 Weeks of Gestation.J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Mar 5;34(10):e77. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e77. eCollection 2019 Mar 18. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30886548 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020 Aug;63(8):284-290. doi: 10.3345/cep.2019.00822. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32023404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N, Siner B, Taylor G, Schluchter M, et al. Improved neurodevelopmental outcomes for extremely low birth weight infants in 2000–2002. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):37–45. - PubMed
-
- Sellier E, Platt MJ, Andersen GL, Krägeloh-Mann I, De La Cruz J, Cans C, et al. Decreasing prevalence in cerebral palsy: a multi-site European population-based study, 1980 to 2003. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58(1):85–92. - PubMed
-
- Chang YS, Ahn SY, Park WS. The Establishment of the Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) Neonatal Med. 2013;20(2):169–178.
-
- The Executive Committee of Korean Neonatal Network. 2013 Korean Neonatal Network Annual Report. Cheongju: Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2013.
-
- The Executive Committee of Korean Neonatal Network. 2014 Korean Neonatal Network Annual Report. Cheongju: Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2014.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

