Relevance of Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors on Trypanosoma cruzi Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and In Silico Integrated Approach
- PMID: 30473742
- PMCID: PMC6220389
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8676578
Relevance of Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors on Trypanosoma cruzi Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and In Silico Integrated Approach
Abstract
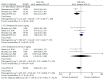
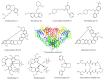
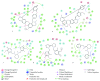
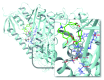
Due to the rudimentary antioxidant defenses in Trypanosoma cruzi, disruptors of redox balance are promising candidates for new antitrypanosomal drugs. We developed an integrated model based on systematic review, meta-analyses, and molecular modeling to evaluate the effect of trypanothione reductase (TR) inhibitors in T. cruzi infections. Our findings indicated that the TR inhibitors analyzed were effective in reducing parasitemia and mortality due to Trypanosoma cruzi infection in animal models. The most investigated drugs (clomipramine and thioridazine) showed no beneficial effects on the occurrence of infection-related electrocardiographic abnormalities or the affinity and density of cardiac β-adrenergic receptors. The affinity between the tested ligands and the active site of TR was confirmed by molecular docking. However, the molecular affinity score was unable to explain TR inhibition and T. cruzi death in vitro or the antiparasitic potential of these drugs when tested in preclinical models of T. cruzi infection. The divergence of in silico, in vitro, and in vivo findings indicated that the anti-T. cruzi effects of the analyzed drugs were not restricted to TR inhibition. As in vivo studies on TR inhibitors are still scarce and exhibit methodological limitations, mechanistic and highly controlled studies are required to improve the quality of evidence.
Figures









References
-
- Pereira R. M., Greco G. M. Z., Moreira A. M., et al. Applicability of plant-based products in the treatment of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei infections: a systematic review of preclinical in vivo evidence. Parasitology. 2017;144(10):1275–1287. doi: 10.1017/S0031182017000634. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO. Chagas Disease. World Health Organization; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

