Frequent blood donations alter susceptibility of red blood cells to storage- and stress-induced hemolysis
- PMID: 30474858
- PMCID: PMC6347021
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.14998
Frequent blood donations alter susceptibility of red blood cells to storage- and stress-induced hemolysis
Abstract
Background: Frequent whole blood donations increase the prevalence of iron depletion in blood donors, which may subsequently interfere with normal erythropoiesis. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the associations between donation frequency and red blood cell (RBC) storage stability in a racially/ethnically diverse population of blood donors.
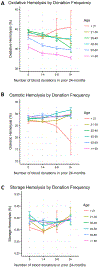
Study design: Leukoreduced RBC concentrate-derived samples from 13,403 donors were stored for 39 to 42 days (1-6°C) and then evaluated for storage, osmotic, and oxidative hemolysis. Iron status was evaluated by plasma ferritin measurement and self-reported intake of iron supplements. Donation history in the prior 2 years was obtained for each subject.
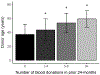
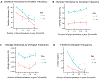
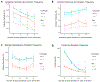
Results: Frequent blood donors enrolled in this study were likely to be white, male, and of older age (56.1 ± 5.0 years). Prior donation intensity was negatively associated with oxidative hemolysis (p < 0.0001) in multivariate analyses correcting for age, sex, and race/ethnicity. Increased plasma ferritin concentration was associated with increased RBC susceptibility to each of the three measures of hemolysis (p < 0.0001 for all), whereas self-reported iron intake was associated with reduced susceptibility to osmotic and oxidative hemolysis (p < 0.0001 for both).
Conclusions: Frequent blood donations may alter the quality of blood components by modulating RBC predisposition to hemolysis. RBCs collected from frequent donors with low ferritin have altered susceptibility to hemolysis. Thus, frequent donation and associated iron loss may alter the quality of stored RBC components collected from iron-deficient donors. Further investigation is necessary to assess posttransfusion safety and efficacy in patients receiving these RBC products.
© 2018 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Translating red cell "omics" into new perspectives in transfusion medicine: mining the gems in the data mountains.Transfusion. 2019 Jan;59(1):2-5. doi: 10.1111/trf.15066. Transfusion. 2019. PMID: 30615814 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jordan A, Chen D, Yi QL, Kanias T, Gladwin MT, Acker JP. Assessing the influence of component processing and donor characteristics on quality of red cell concentrates using quality control data. Vox Sang 2016;111: 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Tzounakas VL, Georgatzakou HT, Kriebardis AG, Voulgaridou AI, Stamoulis KE, Foudoulaki-Paparizos LE, Antonelou MH, Papassideri IS. Donor variation effect on red blood cell storage lesion: a multivariable, yet consistent, story. Transfusion 2016;56: 1274–86. - PubMed
-
- Kanias T, Lanteri MC, Page GP, Guo Y, Endres SM, Stone M, Keating S, Mast AE, Cable RG, Triulzi DJ, Kiss JE, Murphy EL, Kleinman S, Busch MP, Gladwin MT. Ethnicity, sex, and age are determinants of red blood cell storage and stress hemolysis: results of the REDS-III RBC-Omics study. Blood Adv 2017;1: 1132–41. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kiss JE, Birch RJ, Steele WR, Wright DJ, Cable RG. Quantification of body iron and iron absorption in the REDS-II Donor Iron Status Evaluation (RISE) study. Transfusion 2017;57: 1656–64. - PubMed

