Chiral Syn-1,3-diol Derivatives via a One-Pot Diastereoselective Carboxylation/ Bromocyclization of Homoallylic Alcohols
- PMID: 30476789
- PMCID: PMC6257933
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.11.010
Chiral Syn-1,3-diol Derivatives via a One-Pot Diastereoselective Carboxylation/ Bromocyclization of Homoallylic Alcohols
Abstract
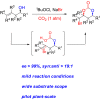
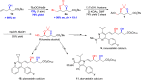
Chiral syn-1,3-diols are fundamental structural motifs in many natural products and drugs. The traditional Narasaka-Prasad diastereoselective reduction from chiral β-hydroxyketones is an important process for the synthesis of these functionalized syn-1,3-diols, but it is of limited applicability for large-scale synthesis because (1) highly diastereoselective control requires extra explosive and flammable Et2BOMe as a chelating agent under cryogenic conditions and (2) only a few functional syn-1,3-diol scaffolds are available. Those involving halogen-functionalized syn-1,3-diols are much less common. There are no reported diastereoselective reactions involving chemical fixation of CO2/bromocyclization of homoallylic alcohols to halogen-containing chiral syn-1,3-diols. Herein, we report an asymmetric synthesis of syn-1,3-diol derivatives via direct diastereoselective carboxylation/bromocyclization with both relative and absolute stereocontrol utilizing chiral homoallylic alcohols and CO2 in one pot with up to 91% yield, > 99% ee, and >19:1 dr. The power of this methodology has been demonstrated by the asymmetric synthesis of statins at the pilot plant scale.
Keywords: Chemistry; Organic Chemistry; Stereochemistry.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad M., Bergstrom R.C., Cashen M.J., McClelland R.A., Powell M.F. “Phosphate extension”. A strategem for the stereoselective functionalization of acyclic homoallylic alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977;99:4829–4830.
-
- Angelo M.L., Moreira L.M., Ruela A.L.M., Morais A.L., Santos A.L.A., Salgado H.R.N., Magali B.A. Analytical methods for the determination of rosuvastatin in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids: a critical review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018;48:317–329. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett P.A., Meadows J.D., Brown E.G., Morimoto A., Jernstedt K.K. Carbonate extension. A versatile procedure for functionalization of acyclic homoallylic alcohols with moderate stereocontrol. J. Org. Chem. 1982;47:4013–4018.
-
- Beck G., Jendralla H., Kesseler K. Practical large scale synthesis of tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-hydroxy-3,5-O-isopropylidene-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate: essential building block for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Synthesis. 1995;8:1014–1018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

