Assessment of Patient and Occupational Safety Culture in Hospitals: Development of a Questionnaire with Comparable Dimensions and Results of a Feasibility Study in a German University Hospital
- PMID: 30477111
- PMCID: PMC6313355
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15122625
Assessment of Patient and Occupational Safety Culture in Hospitals: Development of a Questionnaire with Comparable Dimensions and Results of a Feasibility Study in a German University Hospital
Abstract
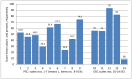
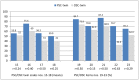
(1) Background: Both patient and occupational safety cultures should be considered when promoting safety culture. To our knowledge, there are no studies that capture patient safety culture (PSC) and occupational safety culture (OSC) in hospitals while using a common questionnaire. The aim of this feasibility study in a German university hospital was to develop a questionnaire to assess both issues analogously. In addition to feasibility outcomes, we report results of PSC-OSC comparisons. (2) Methods: To assess PSC, we used the existing Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture (HSPSC) questionnaire. Developing new OSC "twin items" for certain parts of the HSPSC was supported by a previous literature review. Additionally, we developed multiple choice questions to examine knowledge and competencies regarding specific PS/OS aspects. (3) Results: Developing and implementing a combined PSC and OSC assessment instrument was feasible. The overall response rate was 33% (407 nurses, 140 physicians). In general, the statistical reliability of almost all scales was sufficient. Positive PSC perceptions (agreement rates 46⁻87%) were found in 16 out of 18 scales. Of the four twin scales, the PSC values were significantly better. Individual PS- and OS-related knowledge and competencies were lower than expected. (4) Conclusion: The comparative investigation of patient and occupational safety in a large hospital is a promising approach and can be recommended for further studies. We used our experiences that are presented here in an ongoing bicentric study on the associations between working conditions, occupational safety culture, patient safety culture, and patient safety outcomes (WorkSafeMed).
Keywords: feasibility study; health care workers; hospital; instrument development; occupational safety culture; patient safety culture; survey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Health & Safety Commission . ACSNI Human Factors Study Group Third Report: Organising for Safety. HMSO; London, UK: 1993.
-
- Wagner C., Mannion R., Hammer A., Groenes O., Arah O.A., Dersarkissian M., Sunol R., Duque Project Consortium The associations between organizational culture, organizational structure and quality management in European hospitals. Int. J. Qual. Health Care. 2014;26:74–80. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzu027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorra J., Nieva V.F. Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture. AHRQ Publication No. 04-0041; Rockville, MD, USA: 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

