Effects of tumor metabolic microenvironment on regulatory T cells
- PMID: 30477520
- PMCID: PMC6260778
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0913-y
Effects of tumor metabolic microenvironment on regulatory T cells
Abstract
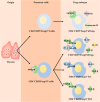
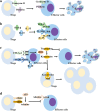
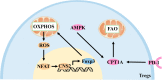
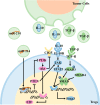
Recent studies have shown that on one hand, tumors need to obtain a sufficient energy supply, and on the other hand they must evade the body's immune surveillance. Because of their metabolic reprogramming characteristics, tumors can modify the physicochemical properties of the microenvironment, which in turn affects the biological characteristics of the cells infiltrating them. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are a subset of T cells that regulate immune responses in the body. They exist in large quantities in the tumor microenvironment and exert immunosuppressive effects. The main effect of tumor microenvironment on Tregs is to promote their differentiation, proliferation, secretion of immunosuppressive factors, and chemotactic recruitment to play a role in immunosuppression in tumor tissues. This review focuses on cell metabolism reprogramming and the most significant features of the tumor microenvironment relative to the functional effects on Tregs, highlighting our understanding of the mechanisms of tumor immune evasion and providing new directions for tumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: Cancer metabolism microenvironment; Hypoxia; Low pH; Regulatory T cells; Signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Tu C, Zeng Z, Qi P, Li X, Guo C, Xiong F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Liao Q, Yu J, et al. Identification of genomic alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived Epstein-Barr virus by whole genome sequencing. Carcinogenesis. 2018; 10.1093/carcin/bgy108. - PubMed
-
- Zou Guoying, Ren Biqiong, Liu Yi, Fu Yin, Chen Pan, Li Xiayu, Luo Shudi, He Junyu, Gao Ge, Zeng Zhaoyang, Xiong Wei, Li Guiyuan, Huang Yumei, Xu Keqian, Zhang Wenling. Inhibin B suppresses anoikis resistance and migration through the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Science. 2018;109(11):3416–3427. doi: 10.1111/cas.13780. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

