Long-term clinical outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting with pedicled saphenous vein grafts
- PMID: 30477543
- PMCID: PMC6258143
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-018-0800-z
Long-term clinical outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting with pedicled saphenous vein grafts
Abstract
Background: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) using saphenous vein grafts (SVG) is vitiated by poor long-term patency of the vein grafts. Pedicled SVG harvested with the "no-touch" (NT) technique have demonstrated improved patency and could confer better outcomes. We aim to compare long-term results after CABG where NT or conventional technique was used for vein graft harvesting in a hypothesis-generating registry-based study.
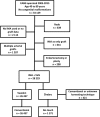
Methods: Two propensity score matched cohorts (1349 patients) undergoing CABG with veins harvested with NT (NTT) or conventional (CT) technique in Sweden over the period 2005-2015 were used to compare long-term outcomes. Mortality, postoperative incidence of coronary angiography and need for reintervention was recorded and multivariable hazard ratios adjusted for risk factors were calculated.
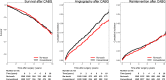
Results: The mean follow-up time (SD) was 6.8 (3.3) years for NTT and 6.6 (3.2) years for CT. The adjusted hazard ratios for death, first angiography and need for reintervention for NTT patients were (95% CI) 0.97 (0.80-1.19), 0.76 (0.63-0.93), 0.91 (0.78-1.05), and 0.91 (0.71-1.17), respectively. Failed grafts were found in 43.2% of NTT patients and 53.6% of CT patients at angiography.
Conclusions: In this study NT grafting was associated with a lower risk for repeat angiography, however no difference could be observed for mortality and need for reintervention. The earlier reported improvements in patency of NT veins could possibly be reflected in an improved clinical outcome during the first 10 years after surgery.
Keywords: CABG; Coronary artery bypass grafting; No-touch; Pedicled vein grafts.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the regional Human Research Ethics Committee, Uppsala, Sweden.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Mohr FW, Morice MC, Kappetein AP, Feldman TE, Stahle E, Colombo A, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft surgery versus percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with three-vessel disease and left main coronary disease: 5-year follow-up of the randomised, clinical SYNTAX trial. Lancet. 2013;381:629–638. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60141-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kolh P, Windecker S, Alfonso F, Collet JP, Cremer J, Falk V, et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task force on myocardial revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;46:517–592. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezu366. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Makikallio T, Holm NR, Lindsay M, Spence MS, Erglis A, Menown IB, et al. Percutaneous coronary angioplasty versus coronary artery bypass grafting in treatment of unprotected left main stenosis (NOBLE): a prospective, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2743–2752. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32052-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

