Sialylation is involved in cell fate decision during development, reprogramming and cancer progression
- PMID: 30478534
- PMCID: PMC6626595
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-018-0597-5
Sialylation is involved in cell fate decision during development, reprogramming and cancer progression
Abstract
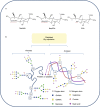
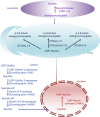
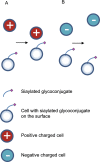
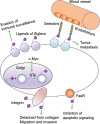
Sialylation, or the covalent addition of sialic acid to the terminal end of glycoproteins, is a biologically important modification that is involved in embryonic development, neurodevelopment, reprogramming, oncogenesis and immune responses. In this review, we have given a comprehensive overview of the current literature on the involvement of sialylation in cell fate decision during development, reprogramming and cancer progression. Sialylation is essential for early embryonic development and the deletion of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase, a rate-limiting enzyme in sialic acid biosynthesis, is embryonically lethal. Furthermore, the sialyltransferase ST6GAL1 is required for somatic cell reprogramming, and its downregulation is associated with decreased reprogramming efficiency. In addition, sialylation levels and patterns are altered during cancer progression, indicating the potential of sialylated molecules as cancer biomarkers. Taken together, the current evidences demonstrate that sialylation is involved in crucial cell fate decision.
Keywords: cancer; cell fate; development; reprogramming; sialylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Fenjie Li and Junjun Ding declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Angata T, Varki A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem Rev. 2002;102(2):439–469. - PubMed
-
- Angata T, Kerr SC, Greaves DR, Varki NM, Crocker PR, Varki A. Cloning and characterization of human Siglec-11. A recently evolved signaling molecule that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages, including brain microglia. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(27):24466–24474. - PubMed
-
- Badr HA, Alsadek DM, Darwish AA, Elsayed AI, Bekmanov BO, Khussainova EM, Zhang X, Cho WC, Djansugurova LB, Li CZ. Lectin approaches for glycoproteomics in FDA-approved cancer biomarkers. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014;11(2):227–236. - PubMed
-
- Baldus SE, Zirbes TK, Monig SP, Engel S, Monaca E, Rafiqpoor K, Hanisch FG, Hanski C, Thiele J, Pichlmaier H, et al. Histopathological subtypes and prognosis of gastric cancer are correlated with the expression of mucin-associated sialylated antigens: Sialosyl-Lewis(a), Sialosyl-Lewis(x) and sialosyl-Tn. Tumour Biol. 1998;19(6):445–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

