Molecular mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review
- PMID: 30478914
- PMCID: PMC6767051
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.32020
Molecular mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review
Abstract
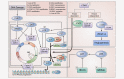
Deregulation of the cyclin D-CDK4/6-INK4-RB pathway leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation, is frequently observed in breast cancer. Currently, three selective CDK4/6 inhibitors have been FDA approved: palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib. Despite promising clinical outcomes, intrinsic or acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors has limited the success of these treatments; therefore, the development of various strategies to overcome this resistance is of great importance. We highlight the various mechanisms that are directly or indirectly responsible for resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, categorizing them into two broad groups; cell cycle-specific mechanisms and cell cycle-nonspecific mechanisms. Elucidation of the diverse mechanisms through which resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors occurs, may aid in the design of novel therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes. This review summarizes the currently available knowledge regarding mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and possible therapeutic strategies that may overcome this resistance as well.
Keywords: CDK4/6; drug resistance; estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.
© 2018 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Figures

References
-
- Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z, Salehiniya H. Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2016;17:43–6. - PubMed
-
- Hart CD, Migliaccio I, Malorni L, et al. Challenges in the management of advanced, ER‐positive, HER2‐negative breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2015;12:541–52. - PubMed
-
- Flaum LE, Gradishar WJ. Advances in endocrine therapy for postmenopausal metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2018;173:141–54. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann J, Bohlmann R, Heinrich N, et al. Characterization of new estrogen receptor destabilizing compounds: effects on estrogen‐sensitive and tamoxifen‐resistant breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004;96:210–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

