Is oxidative stress of adipocytes a cause or a consequence of the metabolic syndrome?
- PMID: 30479968
- PMCID: PMC6240632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2018.11.001
Is oxidative stress of adipocytes a cause or a consequence of the metabolic syndrome?
Abstract
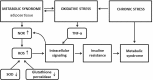
Metabolic syndrome is accompanied by oxidative stress in animals and humans. The main source of ROS in experimental metabolic syndrome is NADPH oxidase and possibly adipocyte mitochondria. It is now documented that oxidative stress induces insulin resistance of adipocytes and increases secretion of leptin, MCP-1, IL-6, and TNF-α by adipocytes. It was established that oxidative stress induces a decrease in adiponectin production by adipocytes. It has also been shown that obesity itself can induce oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can cause an alteration of intracellular signaling in adipocytes that apparently leads to the formation of insulin resistance of adipocytes. Chronic stress, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, angiotensin-II, TNF-α also play an important role in the pathogenesis of oxidative stress of adipocytes. Oxidative stress is not only a consequence of metabolic syndrome, but also a reason and a foundational link in the pathogenesis of the metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Adipocytes; Metabolic syndrome; Oxidative stress.
Figures
References
-
- Beck-Nielsen H. Introduction and definition of the metabolic syndrome. In: Beck-Nielsen H., editor. The metabolic syndrome: pharmacology and clinical aspects. Springer-Verlag; Wien: 2013. pp. 1–6.
-
- Aguilar M., Bhuket T., Torres S., Liu B., Wong R.J. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the United States, 2003–2012. JAMA. 2015;313(19):1973–1974. - PubMed
-
- Block A., Schipf S., Van der Auwera S., Hannemann A., Nauck M., John U. Sex- and age-specific associations between major depressive disorder and metabolic syndrome in two general population samples in Germany. Nord J Psychiatry. 2016;70(8):611–620. - PubMed
-
- Mitrofanov I.M., Seliatitskaia V.G., Nikolaev IuA, Lutov IuV. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in an organized population. Klin Med (Mosk) 2012;90(11):47–50. - PubMed
-
- Isomaa B., Almgren P., Tuomi T., Forsén B., Lahti K., Nissén M. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diab Care. 2001;24(4):683–689. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous