A phase I study of TAS-205 in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 30480028
- PMCID: PMC6243382
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.651
A phase I study of TAS-205 in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Objective: Currently, the only approved standard Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) treatment in Japan is oral steroids, which have various disadvantages. Previous work has suggested that hematopoietic-type prostaglandin D synthase (HPGDS), involved in production of the inflammatory mediator prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), might have a role in DMD pathology. We therefore investigated the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics of a highly selective HPGDS inhibitor (TAS-205) in Japanese patients with genetically confirmed DMD.
Methods: This was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase I study to evaluate the use of single or 7-day repeated doses of TAS-205 administered orally. The urinary excretion of PGD2 metabolites was also assessed.
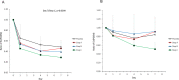
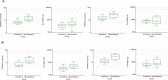
Results: The PK analysis set included 15 and 14 patients in the single- and repeated-dose periods, respectively; the pharmacodynamics set and the safety set included 21 and 19 patients in each period, respectively. The PK of TAS-205 were linear in the dose range studied (1.67-13.33 mg/kg/dose) and the plasma concentration of TAS-205 reached steady state by Day 4. TAS-205 dose-dependently decreased the urinary excretion of tetranor-prostaglandin D metabolite at each measurement time point and did not affect the urinary excretion of tetranor-prostaglandin E metabolite. No clinically significant adverse events were reported after TAS-205 single or repeated administration.
Interpretation: We confirmed the safety and tolerability of TAS-205 in this study. TAS-205 decreased the total urinary excretion of PGD2 metabolites in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that TAS-205 might be a therapeutic option to treat DMD patients.
Figures




References
-
- Hoffman EP, Brown RH Jr, Kunkel LM. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 1987;51:919–928. - PubMed
-
- Theadom A, Rodrigues M, Roxburgh R, et al. Prevalence of muscular dystrophies: a systematic literature review. Neuroepidemiology 2014;43:259–268. - PubMed
-
- Evans NP, Misyak SA, Robertson JL, et al. Dysregulated intracellular signaling and inflammatory gene expression during initial disease onset in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2009;88:502–522. - PubMed
-
- Urade Y, Hayaishi O. Prostaglandin D synthase: structure and function. Vitam Horm 2000;58:89–120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

