Cervical skin denervation associates with alpha-synuclein aggregates in Parkinson disease
- PMID: 30480033
- PMCID: PMC6243385
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.669
Cervical skin denervation associates with alpha-synuclein aggregates in Parkinson disease
Abstract
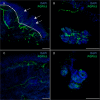
Objective: Autonomic nervous system is involved at the onset of Parkinson disease (PD), and alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) and its phosphorylated form (p-αSyn) have been detected in dermal autonomic nerve fibers of PD. We assessed disease specific conformation variant of α-Syn immunoreactivity in cutaneous nerves and characterized skin denervation patterns in PD and atypical parkinsonism (AP).
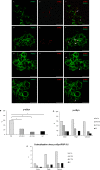
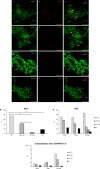
Methods: We enrolled 49 subjects, 19 with PD, 17 age-matched healthy controls, and 13 with AP. The manifestations of disease were rated on clinical scales. Skin biopsies from ankle, thigh, and neck were analyzed by immunofluorescence for p-αSyn, 5G4 as a conformation specific antibody to pathogenic α-Syn and PGP9.5 as axonal marker. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density was measured in all anatomical sites as marker of neurodegeneration. Thirteen of the 19 PD underwent a 1 year follow-up visit plus skin biopsies.
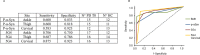
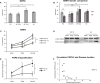
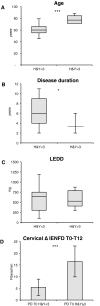
Results: PD subjects displayed more severe cervical skin denervation (P < 0.03), which correlated to disease duration and worsened between initial and follow-up examination (P < 0.001). p-αSyn and 5G4 were equally sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of PD (area under the ROC was 0.839 for p-αSyn and 0.886 for 5G4). PD and AP with possible alpha-synucleinopathies share the features of marked cervical denervation and the presence of 5G4. In contrast AP with possible tauopathies were normal.
Interpretation: Conformational specific forms of α-Syn are detectable in skin biopsy by immunofluorescence in PD, with a promising diagnostic efficiency similar to p-αSyn. Cervical cutaneous denervation correlates with disease duration and increases over time standing out as a potential biomarker of PD progression.
Figures
References
-
- Braak H, Rub U, Gai WP, Del Tredici K. Idiopathic Parkinson's disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2003;110:517–536. - PubMed
-
- Kihara M, Kihara Y, Tukamoto T, et al. Assessment of sudomotor dysfunction in early Parkinson's disease. Eur Neurol 1993;33:363–365. - PubMed
-
- Swinn L, Schrag A, Viswanathan R, et al. Sweating dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2003;18:1459–1463. - PubMed

