Detection of local and remote cellular damage caused by spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury using a heat shock signaling reporter system
- PMID: 30480161
- PMCID: PMC6240805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibror.2018.11.003
Detection of local and remote cellular damage caused by spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury using a heat shock signaling reporter system
Abstract
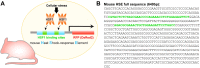
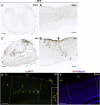
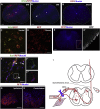
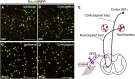
Spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury results in extensive damage to the locally injured cells as well as distant cells that are functionally connected to them. Both primary and secondary damage can cause a broad range of clinical abnormalities, including neuropathic pain and cognitive and memory dysfunction. However, the mechanisms underlying these abnormalities remain unclear, awaiting new methods to identify affected cells to enable examination of their molecular, cellular and physiological characteristics. Here, we report that both primary and secondary damage to cells in mouse models of spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury can be detected in vivo using a novel fluorescent reporter system based on the immediate stress response via activation of Heat Shock Factor 1. We also provide evidence for altered electrophysiological properties of reporter-positive secondarily-injured neurons. The comprehensive identification of injured, but surviving cells located both close and at distant locations from the injury site in vivo will provide a way to study their pathophysiology and possibly prevention of their further deterioration.
Keywords: Cellular damage; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; FG, Fluoro-Gold; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; HSE, heat shock-response element; HSF1, heat shock factor 1; HSP, heat shock protein; Heat shock signaling; IL-6, interleukin 6; M1, primary motor cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; MPtA, medial parietal association cortex; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; RFP, red fluorescent protein; Reporter mouse; SCI, spinal cord injury; SNI, sciatic nerve injury; Sciatic nerve injury; Spinal cord injury; WDR, wide-dynamic range; WGA, wheat germ agglutinin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regeneration of dorsal root axons into experimentally altered glial environments in the rat spinal cord.Exp Brain Res. 1994;99(1):25-33. doi: 10.1007/BF00241409. Exp Brain Res. 1994. PMID: 7523172
-
Increased Expression of Fibronectin Leucine-Rich Transmembrane Protein 3 in the Dorsal Root Ganglion Induces Neuropathic Pain in Rats.J Neurosci. 2019 Sep 18;39(38):7615-7627. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0295-19.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31346030 Free PMC article.
-
HBO treatment enhances motor function and modulates pain development after sciatic nerve injury via protection the mitochondrial function.J Transl Med. 2023 Aug 15;21(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04414-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37582750 Free PMC article.
-
Basic mechanisms of peripheral nerve injury and treatment via electrical stimulation.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Oct;17(10):2185-2193. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.335823. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35259827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathobiology of neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct 19;429(1-3):23-37. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01303-6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11698024 Review.
Cited by
-
Tracking the Activation of Heat Shock Signaling in Cellular Protection and Damage.Cells. 2022 May 5;11(9):1561. doi: 10.3390/cells11091561. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563865 Free PMC article.
-
HSF1 is involved in suppressing A1 phenotype conversion of astrocytes following spinal cord injury in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Sep 16;18(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02271-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34530848 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3a as a sensor of unilateral nerve injury in sensory neurons ipsilateral, contralateral and remote to injury.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Dec;15(12):2353-2361. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.284999. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 32594060 Free PMC article.
-
When the left side knows something happened to the right - sensing injury in neurons contralateral and remote to injury.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Oct;15(10):1854-1855. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.280316. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 32246633 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Long-term spatial tracking of cells affected by environmental insults.J Neurodev Disord. 2020 Dec 16;12(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s11689-020-09339-w. J Neurodev Disord. 2020. PMID: 33327938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalfie M., Kain S.R. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken: 2005. Green Fluorescent Protein: Properties, Applications and Protocols.
-
- Chang Y.W., Waxman S.G. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and central sensitization following peripheral second-degree burn injury. J. Pain. 2010;11:1146–1154. - PubMed
-
- Colleoni M., Sacerdote P. Murine models of human neuropathic pain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1802:924–933. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

