First-line drugs inhibiting the renin angiotensin system versus other first-line antihypertensive drug classes for hypertension
- PMID: 30480768
- PMCID: PMC6516995
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008170.pub3
First-line drugs inhibiting the renin angiotensin system versus other first-line antihypertensive drug classes for hypertension
Update in
-
First-line diuretics versus other classes of antihypertensive drugs for hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 13;7(7):CD008161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008161.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37439548 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: This is the first update of a Cochrane Review first published in 2015. Renin angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors include angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and renin inhibitors. They are widely prescribed for treatment of hypertension, especially for people with diabetes because of postulated advantages for reducing diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Despite widespread use for hypertension, the efficacy and safety of RAS inhibitors compared to other antihypertensive drug classes remains unclear.
Objectives: To evaluate the benefits and harms of first-line RAS inhibitors compared to other first-line antihypertensive drugs in people with hypertension.
Search methods: The Cochrane Hypertension Group Information Specialist searched the following databases for randomized controlled trials up to November 2017: the Cochrane Hypertension Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE (from 1946), Embase (from 1974), the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.gov. We also contacted authors of relevant papers regarding further published and unpublished work. The searches had no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: We included randomized, active-controlled, double-blinded studies (RCTs) with at least six months follow-up in people with elevated blood pressure (≥ 130/85 mmHg), which compared first-line RAS inhibitors with other first-line antihypertensive drug classes and reported morbidity and mortality or blood pressure outcomes. We excluded people with proven secondary hypertension.
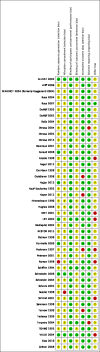
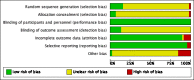
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected the included trials, evaluated the risks of bias and entered the data for analysis.
Main results: This update includes three new RCTs, totaling 45 in all, involving 66,625 participants, with a mean age of 66 years. Much of the evidence for our key outcomes is dominated by a small number of large RCTs at low risk for most sources of bias. Imbalances in the added second-line antihypertensive drugs in some of the studies were important enough for us to downgrade the quality of the evidence.Primary outcomes were all-cause death, fatal and non-fatal stroke, fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), fatal and non-fatal congestive heart failure (CHF) requiring hospitalizations, total cardiovascular (CV) events (fatal and non-fatal stroke, fatal and non-fatal MI and fatal and non-fatal CHF requiring hospitalization), and end-stage renal failure (ESRF). Secondary outcomes were systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and heart rate (HR).Compared with first-line calcium channel blockers (CCBs), we found moderate-certainty evidence that first-line RAS inhibitors decreased heart failure (HF) (35,143 participants in 5 RCTs, risk ratio (RR) 0.83, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.77 to 0.90, absolute risk reduction (ARR) 1.2%), and that they increased stroke (34,673 participants in 4 RCTs, RR 1.19, 95% CI 1.08 to 1.32, absolute risk increase (ARI) 0.7%). Moderate-certainty evidence showed that first-line RAS inhibitors and first-line CCBs did not differ for all-cause death (35,226 participants in 5 RCTs, RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.09); total CV events (35,223 participants in 6 RCTs, RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.02); and total MI (35,043 participants in 5 RCTs, RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.09). Low-certainty evidence suggests they did not differ for ESRF (19,551 participants in 4 RCTs, RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.05).Compared with first-line thiazides, we found moderate-certainty evidence that first-line RAS inhibitors increased HF (24,309 participants in 1 RCT, RR 1.19, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.31, ARI 1.0%), and increased stroke (24,309 participants in 1 RCT, RR 1.14, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.28, ARI 0.6%). Moderate-certainty evidence showed that first-line RAS inhibitors and first-line thiazides did not differ for all-cause death (24,309 participants in 1 RCT, RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.07); total CV events (24,379 participants in 2 RCTs, RR 1.05, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.11); and total MI (24,379 participants in 2 RCTs, RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.01). Low-certainty evidence suggests they did not differ for ESRF (24,309 participants in 1 RCT, RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.37).Compared with first-line beta-blockers, low-certainty evidence suggests that first-line RAS inhibitors decreased total CV events (9239 participants in 2 RCTs, RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.80 to 0.98, ARR 1.7%), and decreased stroke (9193 participants in 1 RCT, RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.63 to 0.88, ARR 1.7% ). Low-certainty evidence suggests that first-line RAS inhibitors and first-line beta-blockers did not differ for all-cause death (9193 participants in 1 RCT, RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.01); HF (9193 participants in 1 RCT, RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.18); and total MI (9239 participants in 2 RCTs, RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.27).Blood pressure comparisons between first-line RAS inhibitors and other first-line classes showed either no differences or small differences that did not necessarily correlate with the differences in the morbidity outcomes.There is no information about non-fatal serious adverse events, as none of the trials reported this outcome.
Authors' conclusions: All-cause death is similar for first-line RAS inhibitors and first-line CCBs, thiazides and beta-blockers. There are, however, differences for some morbidity outcomes. First-line thiazides caused less HF and stroke than first-line RAS inhibitors. First-line CCBs increased HF but decreased stroke compared to first-line RAS inhibitors. The magnitude of the increase in HF exceeded the decrease in stroke. Low-quality evidence suggests that first-line RAS inhibitors reduced stroke and total CV events compared to first-line beta-blockers. The small differences in effect on blood pressure between the different classes of drugs did not correlate with the differences in the morbidity outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Yu Jie Chen: nothing to declare
Liang Jin Li: nothing to declare
Wen Lu Tang: nothing to declare
Jia Yang Song: nothing to declare
Ru Qiu: nothing to declare
Qian Li: nothing to declare
Hao Xue: nothing to declare
James M Wright: nothing to declare
Figures
Update of
-
First-line drugs inhibiting the renin angiotensin system versus other first-line antihypertensive drug classes for hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 11;1:CD008170. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008170.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 14;11:CD008170. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008170.pub3. PMID: 25577154 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
ALLHAT 2002 {published data only}
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Major outcomes in high‐risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 2002;288(23):2981‐97. - PubMed
-
- Barzilay JI, Davis BR, Cutler JA, Pressel SL, Whelton PK, Basile J, et al. Fasting glucose levels and incident diabetes mellitus in older nondiabetic adults randomized to receive 3 different classes of antihypertensive treatment: a report from the Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166(20):2191‐2201. - PubMed
-
- Barzilay JI, Jones CL, Davis BR, Basile JN, Goff DC, Ciocon JO, et al. Baseline characteristics of the diabetic participants in the Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Diabetes Care 2001;24(4):654‐8. - PubMed
-
- Black HR, Davis B, Barzilay J, Nwachuku C, Baimbridge C, Marginean H, et al. Metabolic and clinical outcomes in nondiabetic individuals with the metabolic syndrome assigned to chlorthalidone, amlodipine, or lisinopril as initial treatment for hypertension: a report from the Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Diabetes Care 2008;31(2):353‐60. - PubMed
-
- Cushman WC, Ford CE, Einhorn P, Wright JT, Preston RA, Davis BR, Basile JN. Blood pressure control by randomized drug group in ALLHAT. American Journal of Hypertension 2004;17(5):30A.
Ariff 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ariff B, Zambanini A, Vamadeva S, Barratt D, Xu Y, Sever P, et al. Candesartan‐ and atenolol‐based treatments induce different patterns of carotid artery and left ventricular remodeling in hypertension. Stroke 2006;37(9):2381‐4. - PubMed
BENEDICT 2004 (formerly Ruggenenti 2004) {published data only}
-
- Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, Bruno S, Iliev IP, Brusegan V, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;351(19):1941‐51. - PubMed
Buus 2004 {published data only}
-
- Buus NH, Bottcher M, Jorgensen CG, Christensen KL, Thygesen K, Nielsen TT, et al. Myocardial perfusion during long‐term angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibition or beta‐blockade in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 2004;44(4):465‐70. - PubMed
Buus 2007 {published data only}
-
- Buus NH, Jorgensen CG, Mulvany MJ, Sorensen KE. Large and small artery endothelial function in patients with essential hypertension‐‐effect of ACE inhibition and beta‐blockade. Blood Pressure 2007;16(2):106‐13. - PubMed
Dahlöf 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dahlöf B, Hansson L. The influence of antihypertensive therapy on the structural arteriolar changes in essential hypertension: different effects of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide. Journal of Internal Medicine 1993;234(3):271‐9. - PubMed
Dahlöf 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dahlöf B, Zanchetti A, Diez J, Nicholls MG, Yu CM, Barrios V, et al. Effects of losartan and atenolol on left ventricular mass and neurohormonal profile in patients with essential hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. Journal of Hypertension 2002;20(9):1855‐64. - PubMed
Dalla 2004 {published data only}
-
- Dalla Vestra M, Pozza G, Mosca A, Grazioli V, Lapolla A, Fioretto P, et al. Effect of lercanidipine compared with ramipril on albumin excretion rate in hypertensive Type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria: DIAL study (diabete, ipertensione, albuminuria, lercanidipina). Diabetes Nutrition & Metabolism 2004;17(5):259‐66. - PubMed
Derosa 2004 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Bertone G, Piccinni MN, Fogari E, Ciccarelli L, et al. Comparison of the effects of telmisartan and nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system on blood pressure control, glucose metabolism, and the lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and mild hypertension: a 12‐month, randomized, double‐blind study. Clinical Therapeutics 2004;26(8):1228‐36. - PubMed
Derosa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Gaddi A, Mugellini A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R. Effects of doxazosin and irbesartan on blood pressure and metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2005;45(6):599‐604. - PubMed
Derosa 2014 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Bonaventura A, Bianchi DRL, Fogari E, Angelo AD, Maffioli P. Effects of enalapril/lercanidipine combination on some emerging biomarkers in cardiovascular risk stratification in hypertensive patients. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2014;39:277–85. - PubMed
Devereux 2001 {published data only}
-
- Devereux RB, Palmieri V, Sharpe N, Quattro V, Bella JN, Simone G, et al. Effects of once‐daily angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibition and calcium channel blockade‐based antihypertensive treatment regimens on left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic filling in hypertension: the prospective randomized enalapril study evaluating regression of ventricular enlargement (preserve) trial. Circulation 2001;104(11):1248‐54. - PubMed
Esnault 2008 {published data only}
-
- Esnault VL, Brown EA, Apetrei E, Bagon J, Calvo C, DeChatel R, et al. The effects of amlodipine and enalapril on renal function in adults with hypertension and nondiabetic nephropathies: a 3‐year, randomized, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Clinical Therapeutics 2008;30(3):482‐98. - PubMed
Estacio 1998 {published data only}
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23:B54‐64. - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Hiatt WR, Biggerstaff SL, Gifford N, Schrier RW. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes and hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(10):645‐52. - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Schrier RW. Antihypertensive therapy in type 2 diabetes: implications of the appropriate blood pressure control in diabetes (ABCD) trial. American Journal of Cardiology 1998;82(9b):9r‐14r. - PubMed
Fogari 2012 {published data only}
Gerritsen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gerritsen TA, Bak AA, Stolk RP, Jonker JJ, Grobbee DE. Effects of nitrendipine and enalapril on left ventricular mass in patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16(5):689‐96. - PubMed
Gottdiener 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gottdiener JS, Reda DJ, Williams DW, Materson BJ, Cushman W, Anderson RJ. Effect of single‐drug therapy on reduction of left atrial size in mild to moderate hypertension. Circulation 1998;98(2):140‐8. - PubMed
Hajjar 2013 {published data only}
Hauf‐Zachariou 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hauf‐Zachariou U, Widmann L, Zülsdorf B, Hennig M, Lang PD. A double‐blind comparison of the effects of carvedilol and captopril on serum lipid concentrations in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension and dyslipidaemia. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1993;45(2):95‐100. - PubMed
Hayoz 2012 {published data only}
Himmelmann 1996 {published data only}
-
- Himmelmann A, Hansson L, Hansson BG, Hedstrand H, Skogström K, Ohrvik J, et al. Long‐term renal preservation in essential hypertension. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition is superior to beta‐blockade. American Journal of Hypertension 1996;9(9):850‐3. - PubMed
Hughes 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hughes AD, Stanton AV, Jabbar AS, Chapman N, Martinez‐Perez ME, McG Thom SA. Effect of antihypertensive treatment on retinal microvascular changes in hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2008;26(8):1703‐7. - PubMed
IDNT 2001 {published data only}
-
- Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Lewis JB, Pfeffer MA, Porush JG, Rouleau JL, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;138(7):542‐9. - PubMed
-
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin‐receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345(12):851‐60. - PubMed
LIFE 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dahlöf B, Devereux R, Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Hedner T, Ibsen H, et al. The Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction (LIFE) in Hypertension study: rationale, design, and methods. The LIFE Study Group. American Journal of Hypertension 1997;10(7 Pt 1):705‐13. - PubMed
-
- Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Beevers G, Faire U, et al. Characteristics of 9194 patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: the LIFE study. Losartan Intervention For Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension. Hypertension 1998;32(6):989‐97. - PubMed
-
- Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Beevers G, Faire U, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359(9311):995‐1003. - PubMed
-
- Devereux RB, Dahlöf B, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Aurup P, Beevers G, et al. Effects of losartan or atenolol in hypertensive patients without clinically evident vascular disease: a substudy of the LIFE randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;139(3):169‐77. - PubMed
-
- Fossum E, Moan A, Kjeldsen SE, Devereux RB, Julius S, Snapinn SM, et al. The effect of losartan versus atenolol on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with hypertension taking aspirin: the Losartan Intervention for Endpoint Reduction in hypertension (LIFE) study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2005;46(5):770‐5. - PubMed
Malmqvist 2002 {published data only}
-
- Malmqvist K, Kahan T, Edner M, Bergfeldt L. Comparison of actions of irbesartan versus atenolol on cardiac repolarization in hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy: results from the Swedish Irbesartan Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Investigation Versus Atenolol (SILVHIA). American Journal of Cardiology 2002;90(10):1107‐12. - PubMed
-
- Malmqvist K, Öhman KP, Lind L, Nyström F, Kahan T. Long‐term effects of irbesartan and atenolol on the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system in human primary hypertension: the Swedish Irbesartan Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Investigation versus Atenolol (SILVHIA). Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2003;42:719‐26. - PubMed
-
- Mortsell D, Malmqvist K, Held C, Kahan T. Irbesartan reduces common carotid artery intima‐media thickness in hypertensive patients when compared with atenolol: the Swedish Irbesartan Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Investigation versus Atenolol (SILVHIA) study. Journal of Internal Medicine 2007;261(5):472‐9. - PubMed
NESTOR 2015 {published data only}
-
- Marre M, Puig JG, Kokot F, Fernandez M, Jermendy G, Opie L, et al. Equivalence of indapamide SR and enalapril on microalbuminuria reduction in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes: The NESTOR* study. Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(8):1613‐22. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Agnoletti D, Wang JG, Xu Y, Safar ME. Natriuresis and blood pressure reduction in hypertensive patients with diabetes mellitus: the NESTOR study. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension 2015;9(1):21‐8. - PubMed
Ostman 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ostman J, Asplund K, Bystedt T, Dahlöf B, Jern S, Kjellström T, et al. Comparison of effects of quinapril and metoprolol on glycaemic control, serum lipids, blood pressure, albuminuria and quality of life in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus patients with hypertension. Swedish Quinapril Group. Journal of Internal Medicine 1998;244(2):95‐107. - PubMed
Parrinello 2009 {published data only}
-
- Parrinello G, Paterna S, Torres D, Pasquale P, Mezzero M, Rocca G, et al. One‐year renal and cardiac effects of bisoprolol versus losartan in recently diagnosed hypertensive patients: a randomized, double‐blind study. Clinical Drug Investigation 2009;29(9):591‐600. - PubMed
Pedersen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pedersen EB, Bech JN, Nielsen CB, Kornerup HJ, Hansen HE, Spencer ES, et al. A comparison of the effect of ramipril, felodipine and placebo on glomerular filtration rate, albuminuria, blood pressure and vasoactive hormones in chronic glomerulonephritis. A randomized, prospective, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study over two years. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1997;57(8):673‐81. - PubMed
Petersen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Petersen LJ, Petersen JR, Talleruphuus U, Moller ML, Ladefoged SD, Mehlsen J. A randomized and double‐blind comparison of isradipine and spirapril as monotherapy and in combination on the decline in renal function in patients with chronic renal failure and hypertension. Clinical Nephrology 2001;55:375‐83. - PubMed
Roman 1998 {published data only}
-
- Roman MJ, Alderman MH, Pickering TG, Pini R, Keating JO, Sealey JE, et al. Differential effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and diuretic therapy on reductions in ambulatory blood pressure, left ventricular mass, and vascular hypertrophy. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(4 Pt 1):387‐96. - PubMed
Schiffrin 1994 {published data only}
-
- Schiffrin EL, Deng LY, Larochelle P. Effects of a beta‐blocker or a converting enzyme inhibitor on resistance arteries in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1994;23(1):83‐91. - PubMed
Schmieder 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schmieder RE, Philipp T, Guerediaga J, Gorostidi M, Smith B, Weissbach N, et al. Long‐term antihypertensive efficacy and safety of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren: a 12‐month randomized, double‐blind comparator trial with hydrochlorothiazide. Circulation 2009;119(3):417‐25. - PubMed
Schneider 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schneider MP, Klingbeil AU, Delles C, Ludwig M, Kolloch RE, Krekler M, et al. Effect of irbesartan versus atenolol on left ventricular mass and voltage: results of the CardioVascular Irbesartan Project. Hypertension 2004;44(1):61‐6. - PubMed
Schram 2005 {published data only}
-
- Schram MT, Ittersum FJ, Spoelstra‐de Man A, Dijk RA, Schalkwijk CG, Ijzerman RG, et al. Aggressive antihypertensive therapy based on hydrochlorothiazide, candesartan or lisinopril as initial choice in hypertensive type II diabetic individuals: effects on albumin excretion, endothelial function and inflammation in a double‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Journal of Human Hypertension 2005;19(6):429‐37. - PubMed
Seedat 1998 {published data only}
-
- Seedat YK, Randeree IG. Antihypertensive effect and tolerability of perindopril in Indian hypertensive and type 2 diabetic patients: 1‐year randomised, double‐blind, parallel study vs atenolol. Clinical Drug Investigation 1998;16(3):229‐240. - PubMed
SILVHIA 2001 {published data only}
-
- Malmqvist K, Kahan T, Edner M, Hagg A, Lind L, Muller‐Brunotte R, et al. Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in human hypertension with irbesartan. Journal of Hypertension 2001;19(6):1167‐76. - PubMed
Sørensen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sørensen VB, Rossing P, Tarnow L, Parving H, Nørgaard T, Kastrup J. Effects of nisoldipine and lisinopril on microvascular dysfunction in hypertensive type I diabetes patients with nephropathy. Clinical Science 1998;95(6):709‐17. - PubMed
Tarnow 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tarnow L, Sato A, Ali S, Rossing P, Nielsen FS, Parving HH. Effects of nisoldipine and lisinopril on left ventricular mass and function in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1999;22(3):491‐4. - PubMed
Tedesco 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tedesco MA, Ratti G, Mennella S, Manzo G, Grieco M, Rainone AC, et al. Comparison of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide on cognitive function and quality of life in hypertensive patients. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(11 Pt 1):1130‐4. - PubMed
Terpstra 2004 {published data only}
-
- Terpstra WF, May JF, Smit AJ, Graeff PA, Meyboom‐de Jong B, Crijns HJ. Effects of amlodipine and lisinopril on intima‐media thickness in previously untreated, elderly hypertensive patients (the ELVERA trial). Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(7):1309‐16. - PubMed
TOHMS 1993 {published data only}
-
- Neaton JD, Grimm RH Jr, Prineas RJ, Stamler J, Grandits GA, Elmer PJ, et al. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study. Final results. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study Research Group. JAMA 1993;270(6):713‐24. - PubMed
VALUE 2004 {published data only}
-
- Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M, Brunner HR, Ekman S, Hansson L, et al. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomised trial. Lancet 2004;363(9426):2022‐31. - PubMed
-
- Julius S, Weber MA, Kjeldsen SE, McInnes GT, Zanchetti A, Brunner HR, et al. The Valsartan Antihypertensive Long‐Term Use Evaluation (VALUE) trial: outcomes in patients receiving monotherapy. Hypertension 2006;48(3):385‐91. - PubMed
-
- Mann J, Julius S. The Valsartan Antihypertensive Long‐term Use Evaluation (VALUE) trial of cardiovascular events in hypertension. Rationale and design. Blood Pressure 1998;7(3):176‐83. - PubMed
-
- Sandset E, Krarup LH, Berge E, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Holzhauer B. Predictors of stroke recurrence in high‐risk, hypertensive patients. Journal of Hypertension 2010;28(A):E33.
-
- Zanchetti A, Julius S, Kjeldsen S, McInnes GT, Hua T, Weber M, et al. Outcomes in subgroups of hypertensive patients treated with regimens based on valsartan and amlodipine: an analysis of findings from the VALUE trial. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24(11):2163‐8. - PubMed
Xiao 2016 {published data only}
-
- Xiao WY, Ning N, Tan MH, Jiang XS, Zhou L, Liu L, et al. Effects of antihypertensive drugs losartan and levamlodipine besylate on insulin resistance in patients with essential hypertension combined with isolated impaired fasting glucose. Hypertension Research 2016;39(8):321‐6. - PubMed
Zeltner 2008 {published data only}
-
- Zeltner R, Poliak R, Stiasny B, Schmieder RE, Schulze BD. Renal and cardiac effects of antihypertensive treatment with ramipril vs metoprolol in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2008;23(2):573‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
AASK 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wright JT, Bakris G, Greene T, Agodoa LY, Appel LJ, Charleston J, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease. JAMA 2002;288(19):2421‐31. - PubMed
ANBP2 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chowdhury EK, Owen A, Ademi Z, Krum H, Johnston CI, Wing LMH, et al. Short‐ and long‐term survival in treated elderly hypertensive patients with or without diabetes: findings from the Second Australian National Blood Pressure study. American Journal of Hypertension 2014;27(2):199‐206. - PubMed
-
- Wing LMH, Reid CM, Ryan P, Beilin LJ, Brown MA, Jennings GL, et al. A comparison of outcomes with angiotensin‐converting‐‐enzyme inhibitors and diuretics for hypertension in the elderly. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348:583‐92. - PubMed
Materson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, et al. Single‐drug therapy for hypertension in men. A comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. The Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;328(13):914‐21. - PubMed
Okin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Okin PM, Kjeldsen SE, Lindholm LH, Dahlof B, Devereux RB. The relationship of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy to decreased serum potassium. Blood Pressure 2012;21:146‐52. - PubMed
Peng 2015 {published data only}
-
- Peng J, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Liu Z, Wang Z, Tang M, et al. Prevention of metabolic disorders with telmisartan and indapamide in a Chinese population with high‐normal blood pressure. Hypertension Research 2015;38(2):123‐31. - PubMed
Preston 1998 {published data only}
-
- Preston RA, Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Williams DW, Hamburger RJ, Cushman WC, et al. Age‐race subgroup compared with renin profile as predictors of blood pressure response to antihypertensive therapy. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents. JAMA 1998;280(13):1168‐72. - PubMed
Additional references
ABCD‐HT 2000
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23(suppl 2):B54‐64. - PubMed
ADA 2013
Atkins 2004
-
- Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck‐Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer T, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW Jr, Zaza S, GRADE Working Group. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004;328(7454):1490‐4. - PMC - PubMed
Aurell 1992
-
- Aurell M, Bjorck S. Determinants of progressive renal disease in diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int Suppl 1992;41(suppl 36):S38‐42. - PubMed
CAPPP 2001
-
- Niskanen L, Hedner T, Hansson L, Lanke J, Niklason A, CAPPP Study Group. Reduced cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertensive diabetic patients on first‐line therapy with an ACE inhibitor compared with a diuretic/beta‐blocker‐based treatment regimen: a subanalysis of the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP). Diabetes Care 2001;24:2091‐6. - PubMed
Casas 2005
-
- Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S, Vallance P, Smeeth L, Hingorani AD, et al. Effect of inhibitors of the renin‐angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet 2005;366(9502):2026‐33. - PubMed
Chen 2010
CPG 2013
-
- Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Canadian Diabetes Association 2013 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada ‐ Treatment of Hypertension. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2013;37(Suppl 1):S117‐8. - PubMed
DeStefano 1993
-
- DeStefano F, Ford ES, Newman J, Stevenson JM, Wetterhall SF, Anda RF, et al. Risk factors for coronary heart disease mortality among persons with diabetes. Annals of Epidemiology 1993;3:27‐34. - PubMed
Duprez 2006
-
- Duprez, D. Role of the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system in vascular remodeling and inflammation: a clinical review. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24:983‐91. - PubMed
Dzau 2001
-
- Dzau VJ. Tissue angiotensin and pathobiology of vascular disease: a unifying hypothesis. Hypertension 2001;37:1047‐52. - PubMed
ESH/ESC 2013
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, et al. Task Force Members. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Journal of Hypertension 2013;31(7):1281‐357. - PubMed
Geiss 2002
-
- Geiss LS, Rolka DB, Engelgau MM. Elevated blood pressure among U.S. adults with diabetes, 1988‐1994. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2002;22:42‐8. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
HOPE 2000
-
- Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICROHOPE substudy. Lancet 2000;355:253‐9. - PubMed
Inzucchi 2005
-
- Inzucchi SE, Sherwin RS. The prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America 2005;34(1):199‐219. - PubMed
JNC‐8 2014
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence‐based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014;311(5):507‐20. - PubMed
Kasiske 1993
-
- Kasiske BL, Kalil RS, Ma JZ, Liao M, Keane WF. Effect of antihypertensive therapy on the kidney in patients with diabetes: a meta regression analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993;118(2):129‐38. - PubMed
Kocks 2002
-
- Kocks MJ, Zeeuw D, Navis GJ. Optimal blood pressure control and antihypertensive regimens in hypertensive renal disease. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension 2002;11:135‐40. - PubMed
Li 2014
MARVAL 2002
-
- MARVAL Study Investigators. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2002;106:672‐8. - PubMed
Pahor 2000
-
- Pahor M, Psaty BM, Alderman MH, Applegate WB, Williamson JD, Furberg CD. Therapeutic benefits of ACE inhibitors and other antihypertensive drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23:888‐92. - PubMed
PROGRESS 2001
-
- PROGRESS Collaborative Study Group. Randomised trial of perindopril based blood pressure‐lowering regimen among 6108 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Lancet 2001;358:1033‐41. - PubMed
Ravine 1994
-
- Ravine D, Gibson RN, Walker RG, Sheffield LJ, Kincaid‐Smith P, Danks DM. Evaluation of ultrasonographic diagnostic criteria for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 1. Lancet 1994;343(8901):824‐7. - PubMed
RENAAL 2001
-
- RENAAL Study Investigators. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345:861‐9. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Saha 2008
-
- Saha SA, Molnar J, Arora RR. Tissue angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus without left ventricular systolic dysfunction or clinical evidence of heart failure: a pooled meta‐analysis of randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trials. Diabetes Obesity and Metabolism 2008;10(1):41‐52. - PubMed
Siebenhofer 2004
-
- Siebenhofer A, Plank J, Horvath K, Berghold A, Sutton AJ, Sommer R, et al. Angiotensin receptor blockers as anti‐hypertensive treatment for patients with diabetes mellitus: meta‐analysis of controlled double‐blind randomized trials. Diabetic Medicine 2004;21(1):18‐25. - PubMed
Strippoli 2005
Strippoli 2006
-
- Strippoli GFM, Bonifati C, Craig ME, Navaneethan SD, Craig JC. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006257] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wiysonge 2017
Wright 2009
Wu 2013
-
- Wu HY, Huang JW, Lin HJ, Liao WC, Peng YS, Hung KY, et al. Comparative effectiveness of renin‐angiotensin system blockers and other antihypertensive drugs in patients with diabetes: systematic review and bayesian network meta‐analysis. BMJ 2013;347(7933):f6008. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f6008] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Xue 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous