Cause of Death in Follicular Lymphoma in the First Decade of the Rituximab Era: A Pooled Analysis of French and US Cohorts
- PMID: 30481079
- PMCID: PMC6366812
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.18.00400
Cause of Death in Follicular Lymphoma in the First Decade of the Rituximab Era: A Pooled Analysis of French and US Cohorts
Abstract
Purpose: Although the life expectancy of patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) has increased, little is known of their causes of death (CODs) in the rituximab era.
Patients and methods: We pooled two cohorts of newly diagnosed patients with FL grade 1-3A. Patients were enrolled between 2001 and 2013 in two French referral institutions (N = 734; median follow-up 89 months) and 2002 and 2012 in the University of Iowa and Mayo Clinic Specialized Program of Research Excellence (SPORE; N = 920; median follow-up 84 months). COD was classified as being a result of lymphoma, other malignancy, treatment related, or all other causes.
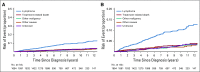
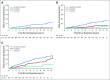
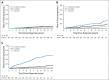
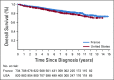
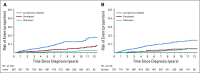
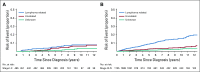
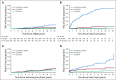
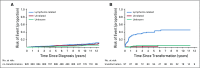
Results: Ten-year overall survival was comparable in the French (80%) and US (77%) cohorts. We were able to classify COD in 248 (88%) of 283 decedents. In the overall cohort, lymphoma was the most common COD, with a cumulative incidence of 10.3% at 10 years, followed by treatment-related mortality (3.0%), other malignancy (2.9%), other causes (2.2%), and unknown (3.0%). The 10-year cumulative incidence of death as a result of lymphoma or treatment was higher than death as a result of all other causes for each age group (including patients ≥ 70 years of age at diagnosis [25.4% v 16.6%]) Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score 3 to 5 (27.4% v 5.2%), but not Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score 0 to 1 (4.0% v 3.7%); for patients who failed to achieve event-free survival within 24 months from diagnosis (36.1% v 7.0%), but not for patients who achieved event-free survival within 24 months of diagnosis (6.7% v 5.7%); and for patients with a history of transformed FL (45.9% v 4.7%), but not among patients without (8.1% v 6.2%). Overall, 77 of 140 deaths as a result of lymphoma occurred in patients whose FL transformed after diagnosis.
Conclusion: Despite the improvement in overall survival in patients with FL in the rituximab era, their leading COD remains lymphoma, especially after disease transformation. Treatment-related mortality also represents a concern, which supports the need for less-toxic therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Roulland S, Faroudi M, Mamessier E, et al. : Early steps of follicular lymphoma pathogenesis. Adv Immunol 111:1-46, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Link BK, Maurer MJ, Nowakowski GS, et al. : Rates and outcomes of follicular lymphoma transformation in the immunochemotherapy era: A report from the University of Iowa/MayoClinic Specialized Program of Research Excellence Molecular Epidemiology Resource. J Clin Oncol 31:3272-3278, 2013 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

