Learning to see the threat: temporal dynamics of ERPs of motivated attention in fear conditioning
- PMID: 30481357
- PMCID: PMC6374602
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsy103
Learning to see the threat: temporal dynamics of ERPs of motivated attention in fear conditioning
Abstract
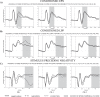
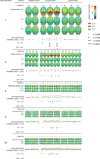
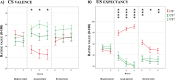
Social threat detection is important in everyday life. Studies of cortical activity have shown that event-related potentials (ERPs) of motivated attention are modulated during fear conditioning. The time course of motivated attention in learning and extinction of fear is, however, still largely unknown. We aimed to study temporal dynamics of learning processes in classical fear conditioning to social cues (neutral faces) by selecting an experimental setup that produces large effects on well-studied ERP components (early posterior negativity, EPN; late positive potential, LPP; stimulus preceding negativity, SPN) and then exploring small consecutive groups of trials. EPN, LPP, and SPN markedly and quickly increased during the acquisition phase in response to the CS+ but not the CS-. These changes were visible even at high temporal resolution and vanished completely during extinction. Moreover, some evidence was found for component differences in extinction learning, with differences between CS+ and CS- extinguishing faster for late as compared to early ERP components. Results demonstrate that fear learning to social cues is a very fast and highly plastic process and conceptually different ERPs of motivated attention are sensitive to these changes at high temporal resolution, pointing to specific neurocognitive and affective processes of social fear learning.
Keywords: affective neuroscience; event-related potentials; fear conditioning; motivated attention; social threat; temporal dynamics.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Brain dynamics of visual attention during anticipation and encoding of threat- and safe-cues in spider-phobic individuals.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015 Sep;10(9):1177-86. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv002. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25608985 Free PMC article.
-
Learning dynamics of electrophysiological brain signals during human fear conditioning.Neuroimage. 2021 Feb 1;226:117569. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117569. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33221446
-
Return of fear following extinction in youth: An event-related potential study.Dev Psychobiol. 2021 Nov;63(7):e22189. doi: 10.1002/dev.22189. Dev Psychobiol. 2021. PMID: 34674235 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitated extinction of conditioned fear responses by delta 9-tetrahyrdrocannabidol in humans: a pilot study.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2022 Nov;37(6):e2853. doi: 10.1002/hup.2853. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35983959 Review.
-
Updated meta-analysis of classical fear conditioning in the anxiety disorders.Depress Anxiety. 2015 Apr;32(4):239-53. doi: 10.1002/da.22353. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Depress Anxiety. 2015. PMID: 25703487 Review.
Cited by
-
A Brain-To-Brain Mechanism for Social Transmission of Threat Learning.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(28):e2304037. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304037. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37544901 Free PMC article.
-
EEG Microstates in Social and Affective Neuroscience.Brain Topogr. 2024 Jul;37(4):479-495. doi: 10.1007/s10548-023-00987-4. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Brain Topogr. 2024. PMID: 37523005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural dynamics underlying coordination between training-induced habitual and goal-directed responses.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2025 Apr;25(2):344-357. doi: 10.3758/s13415-024-01242-4. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39638922
-
Influence of Perceptual and Conceptual Information on Fear Generalization: A Behavioral and Event-Related Potential Study.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2021 Oct;21(5):1054-1065. doi: 10.3758/s13415-021-00912-x. Epub 2021 May 21. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34021495
-
Fear memory in humans is consolidated over time independently of sleep.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2023 Feb;23(1):100-113. doi: 10.3758/s13415-022-01037-5. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36241964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baas J.M., Kenemans J.L., Bocker K.B., Verbaten M.N. (2002). Threat-induced cortical processing and startle potentiation. Neuroreport, 13(1), 133–137. - PubMed
-
- Blankertz B., Lemm S., Treder M., Haufe S., Muller K.R. (2011). Single-trial analysis and classification of ERP components—a tutorial. Neuroimage, 56(2), 814–825. - PubMed
-
- Blechert J., Michael T., Vriends N., Margraf J., Wilhelm F.H. (2007). Fear conditioning in posttraumatic stress disorder: evidence for delayed extinction of autonomic, experiential, and behavioural responses. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45(9), 2019–2033. - PubMed

