Hindbrain dorsal vagal complex AMPK controls hypothalamic gluco-regulatory transmitter and counter-regulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia
- PMID: 30481553
- PMCID: PMC6309468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.11.016
Hindbrain dorsal vagal complex AMPK controls hypothalamic gluco-regulatory transmitter and counter-regulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia
Abstract
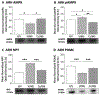
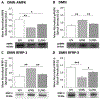
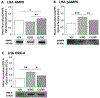
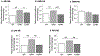
Pharmacologic activation of the hindbrain dorsal vagal complex energy sensor 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) causes site-specific adjustments in hypothalamic AMPK activity. DVC A2 noradrenergic neurons are a likely source of metabolo-sensory cues to downstream network components as they express substrate fuel-sensitive AMPK. This study investigated the hypothesis that DVC AMPK controls hypothalamic sensor, metabolic effector transmitter, and counter-regulatory hormone responses to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Male rats were injected into the caudal fourth ventricle with the AMPK inhibitor compound C (Ccor vehicle before hypoglycemia. Arcuate (ARH), ventromedial (VMN), and dorsomedial (DMN) nuclei and lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) were micropunch-dissected for norepinephrine ELISA and Western blot analyses. Hypoglycemic stimulation of norepinephrine activity in each site was impeded by compound C. Hypoglycemia caused drug-revocable (ARH) or -refractory (VMN, DMN) reductions in AMPK, alongside hindbrain AMPK-dependent augmentation of phospho-AMPK expression in each location. Compound C prevented hypoglycemic augmentation of gluco-stimulatory ARH neuropeptide Y, VMN neuronal nitric oxide synthase, and LHA orexin-A expression, while hypoglycemic suppression of the catabolic neuron protein markers ARH pro-opiomelanocortin and VMN glutamate decarboxylase65/67 was respectively averted or unaffected by drug treatment. DMN RFamide-related peptide-1 and -3 profiles were correspondingly amplified or suppressed hindbrain AMPK-reliant mechanisms during hypoglycemia. Results show that DVC AMPK is required for hypoglycemic intensification of norepinephrine activity in characterized hypothalamic gluco-regulatory structures, and that this sensor regulates AMPK activation and metabolic effector transmission in those sites.
Keywords: AMPK; Compound C; Dopamine-beta hydroxylase; Laser-catapult microdissection; Norepinephrine.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hindbrain lactoprivic regulation of hypothalamic neuron transactivation and gluco-regulatory neurotransmitter expression: Impact of antecedent insulin-induced hypoglycemia.Neuropeptides. 2019 Oct;77:101962. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2019.101962. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Neuropeptides. 2019. PMID: 31488323 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Metabolic-Sensory Neuron 5'-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activity: Impact of Estradiol.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 16;21(6):2013. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062013. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32188013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral but not Medial Hypothalamic AMPK Activation Occurs at the Hypoglycemic Nadir in Insulin-injected Male Rats: Impact of Caudal Dorsomedial Hindbrain Catecholamine Signaling.Neuroscience. 2018 May 21;379:103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 11. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29534973
-
Role of hindbrain adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in hypothalamic AMPK and metabolic neuropeptide adaptation to recurring insulin-induced hypoglycemia in the male rat.Neuropeptides. 2017 Dec;66:25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Neuropeptides. 2017. PMID: 28823463
-
Energy metabolism and hindbrain AMPK: regulation by estradiol.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014 Mar;17(3):129-36. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0067. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014. PMID: 25372736 Review.
Cited by
-
Hindbrain lactoprivic regulation of hypothalamic neuron transactivation and gluco-regulatory neurotransmitter expression: Impact of antecedent insulin-induced hypoglycemia.Neuropeptides. 2019 Oct;77:101962. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2019.101962. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Neuropeptides. 2019. PMID: 31488323 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of caudal hindbrain glycogen metabolism on A2 noradrenergic neuron AMPK activation and ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus norepinephrine activity and glucoregulatory neurotransmitter marker protein expression.Neuropeptides. 2020 Aug;82:102055. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2020.102055. Epub 2020 May 16. Neuropeptides. 2020. PMID: 32451071 Free PMC article.
-
Hindbrain metabolic deficiency regulates ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus glycogen metabolism and glucose‑regulatory signaling.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2020;80(1):57-65. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2020. PMID: 32214275 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine Regulation of Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Metabolic-Sensory Neuron 5'-AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activity: Impact of Estradiol.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 16;21(6):2013. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062013. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32188013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Hypothesis That Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Exert Immediate and Multifaceted Effects by Activating Adenosine Monophosphate-Activate Protein Kinase (AMPK).Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 7;15(2):253. doi: 10.3390/life15020253. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alenazi FSH, Ibrahim BA, Briski KP. Estradiol regulates effects of hindbrain activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-riboside administration on hypothalamic adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity and metabolic neurotransmitter mRNA and protein expression. J. Neurosci. Res 2014; 93: 651–659. - PubMed
-
- Alhamami HN, Uddin MM, Mahmood, ASMH, Briski KP. Lateral but not medial hypothalamic AMPK activation occurs at the hypoglycemic nadir in insulin-injected male rats: Impact of caudal dorsomedial hindbrain catecholamine signaling. Neuroscience 2018; 379: 103–114 - PubMed
-
- Beverly JL, de Vries MG, Beverly MF, Arseneau LM. Norepinephrine mediates glucoprivic-induced increase in GABA in the ventromedial hypothalamus of rats. Amer. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol 2000; 279: R990–R996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

