EWSR1, a multifunctional protein, regulates cellular function and aging via genetic and epigenetic pathways
- PMID: 30481590
- PMCID: PMC6527469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.042
EWSR1, a multifunctional protein, regulates cellular function and aging via genetic and epigenetic pathways
Abstract
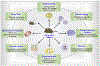
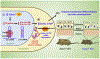
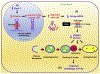
Ewing's sarcoma (EWS) is a bone cancer arising predominantly in young children. EWSR1 (Ewing Sarcoma breakpoint region 1/EWS RNA binding protein 1) gene is ubiquitously expressed in most cell types, indicating it has diverse roles in various cellular processes and organ development. Recently, several studies have shown that missense mutations of EWSR1 genes are known to be associated with central nervous system disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Otherwise, EWSR1 plays epigenetic roles in gene expression, RNA processing, and cellular signal transduction. Interestingly, EWSR1 controls micro RNA (miRNA) levels via Drosha, leading to autophagy dysfunction and impaired dermal development. Ewsr1 deficiency also leads to premature senescence of blood cells and gamete cells with a high rate of apoptosis due to the abnormal meiosis. Despite these roles of EWSR1 in various cellular functions, the exact mechanisms are not yet understood. In this context, the current review overviews a large body of evidence and discusses on what EWSR1 genetic mutations are associated with brain diseases and on how EWSR1 modulates cellular function via the epigenetic pathway. This will provide a better understanding of bona fide roles of EWSR1 in aging and its association with brain disorders.
Keywords: Autophagy; Brain disorders; EWSR1; Epigenetic function; Genetic mutation; miRNA.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Uvrag targeting by Mir125a and Mir351 modulates autophagy associated with Ewsr1 deficiency.Autophagy. 2015;11(5):796-811. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1035503. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25946189 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of autophagy by miRNAs.BMB Rep. 2015 Jul;48(7):371-2. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.7.121. BMB Rep. 2015. PMID: 26129673 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of EWSR1 (Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1/EWS RNA binding protein 1) predicts poor survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):7941-7949. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1982844. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34612781 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Intracranial Ewing Sarcoma Invading the Superior Sagittal Sinus with EWSR1-FLI1 Gene Fusion and EWSR1 Gene Mutation: A Case Report and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2023 Jul;175:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.03.097. Epub 2023 Mar 27. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 36990350 Review.
-
Soft tissue tumors associated with EWSR1 translocation.Virchows Arch. 2010 Feb;456(2):219-34. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0854-3. Virchows Arch. 2010. PMID: 19936782 Review.
Cited by
-
The miR-146b-5p promotes Ewing's sarcoma cells progression via suppressing the expression of BTG2.Sci Prog. 2021 Apr-Jun;104(2):368504211002043. doi: 10.1177/00368504211002043. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 33844600 Free PMC article.
-
A Proximity biotinylation assay with a host protein bait reveals multiple factors modulating enterovirus replication.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Oct 28;18(10):e1010906. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010906. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36306280 Free PMC article.
-
Smart-seq2 Technology Reveals a Novel Mechanism That Zearalenone Inhibits the In Vitro Maturation of Ovine Oocytes by Influencing TNFAIP6 Expression.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 17;15(10):617. doi: 10.3390/toxins15100617. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37888648 Free PMC article.
-
EWSR1-TFCP2 in an adolescent represents an extremely rare and aggressive form of intraosseous spindle cell rhabdomyosarcomas.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2022 Jun 29;8(5):a006209. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a006209. Online ahead of print. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2022. PMID: 35768243 Free PMC article.
-
Lower expression of BIN1's neuronal isoform in vulnerable excitatory neurons increases risk in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Jan 13;9:25424823241296018. doi: 10.1177/25424823241296018. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40034505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plouqastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, de Jong P, Rouleau G, Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours, Nature 359 (1992) 162–165. - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti A, Melot T, Acker J, Vigneron M, Delattre O, Tora L, EWS, but not EWS-FLI-1, is associated with both TFIID and RNA polymerase II: interactions between two members of the TET family, EWS and hTAFII68, and subunits of TFIID and RNA polymerase II complexes, Mol. Cell. Biol 18 (1998) 1489–1497. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rossow KL, Janknecht R, The Ewing’s sarcoma gene product functions as a transcriptional activator, Cancer Res. 61 (2001) 2690–2695. - PubMed
-
- Araya N, Hirota K, Shimamoto Y, Miyagishi M, Yoshida E, Ishida J, Kaneko S, Kaneko M, Nakajima T, Fukamizu A, Cooperative interaction of EWS with CREB-binding protein selectively activates hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-mediated transcription, J. Biol. Chem 278 (2003) 5427–5432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

