The correlation of heart rate between natural sleep and dexmedetomidine sedation
- PMID: 30481949
- PMCID: PMC6458515
- DOI: 10.4097/kja.d.18.00208
The correlation of heart rate between natural sleep and dexmedetomidine sedation
Abstract
Background: Sedation by dexmedetomidine, like natural sleep, often causes bradycardia. We explored the nature of heart rate (HR) changes as they occur during natural sleep versus those occurring during dexmedetomidine sedation.
Methods: The present study included 30 patients who were scheduled to undergo elective surgery with spinal anesthesia. To assess HR and sedation, a pulse oximeter and bispectral index (BIS) monitor were attached to the patient in the ward and the operating room. After measuring HR and BIS at baseline, as the patients slept and once their BIS was below 70, HR and BIS were measured at 5-minute intervals during sleep. Baseline HR and BIS were also recorded before spinal anesthesia measured at 5-minute intervals after dexmedetomidine injection.
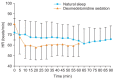
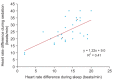
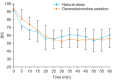
Results: During natural sleep, HR changes ranged from 2 to 19 beats/min (13.4 ± 4.4 beats/min), while in dexmedetomidine sedation, HR ranged from 9 to 40 beats/min (25.4 ± 8.5 beats/min). Decrease in HR was significantly correlated between natural sleep and dexmedetomidine sedation (R2 = 0.41, P < 0.001). The lowest HR was reached in 66 min during natural sleep (59 beats/min) and in 13 min with dexmedetomidine sedation (55 beats/min). The time to reach minimum HR was significantly different (P < 0.001), but there was no difference in the lowest HR obtained (P = 0.09).
Conclusions: There was a correlation between the change in HR during natural sleep and dexmedetomidine sedation. The bradycardia that occurs when using dexmedetomidine may be a normal physiologic change, that can be monitored rather than corrected.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; Heart rate; Sedatives; Sleep; Spinal anesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in First Postoperative Night Bispectral Index After Daytime Sedation Induced by Dexmedetomidine or Midazolam Under Regional Anesthesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016 May-Jun;41(3):380-6. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000370. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016. PMID: 26928796 Clinical Trial.
-
Replacement of dexmedetomidine loading with midazolam for sedation in elderly patients with spinal anesthesia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(39):e12565. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012565. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30278560 Free PMC article.
-
Anticholinergic premedication to prevent bradycardia in combined spinal anesthesia and dexmedetomidine sedation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Dec;35:13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.07.012. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27871510 Clinical Trial.
-
Incidence of bradycardia in pediatric patients receiving dexmedetomidine anesthesia: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Pharm. 2017 Feb;39(1):139-147. doi: 10.1007/s11096-016-0411-5. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Int J Clin Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28040841 Review.
-
The use of dexmedetomidine in anesthesia and intensive care: a review.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(38):6257-65. doi: 10.2174/138161212803832272. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22762468 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitored Anesthesia Care for Cardiovascular Interventions.Korean Circ J. 2020 Jan;50(1):1-11. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0269. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Korean Circ J. 2020. PMID: 31642214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient Comfort During Postop Period in Breast Cancer Surgeries: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Opioid and Opioid-Free Anesthesia.Cureus. 2023 Jan 17;15(1):e33871. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33871. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36819361 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Dexmedetomidine for the Management of Preoperative Anxiety-Related Insomnia: A Randomized, Three-Blinded, Clinical Trial Compared with Lorazepam and Placebo.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 17;18:6061-6073. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S487463. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39717197 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The correlation between the STOP-Bang score and oxygen saturation during spinal anesthesia with dexmedetomidine sedation.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021 Jul;16(3):305-311. doi: 10.17085/apm.21011. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 34289296 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of short-term preoperative intranasal dexmedetomidine plus conventional treatment on delirium following cardiac surgery in patients with sleep disorders.Perioper Med (Lond). 2024 Mar 9;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13741-024-00371-1. Perioper Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38461276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayashi Y, Maze M. Alpha 2 adrenoceptor agonists and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 1993;71:108–18. - PubMed
-
- Aantaa R, Kanto J, Scheinin M, Kallio A, Scheinin H. Dexmedetomidine, an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, reduces anesthetic requirements for patients undergoing minor gynecologic surgery. Anesthesiology. 1990;73:230–5. - PubMed
-
- Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:382–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

