Opportunistic screening models for high-risk men and women to detect diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the community
- PMID: 30482050
- PMCID: PMC6431757
- DOI: 10.1177/2047487318816774
Opportunistic screening models for high-risk men and women to detect diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the community
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of undetected left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is high, especially in the elderly with comorbidities. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction is a prognostic indicator of heart failure, in particularly of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and of future cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Therefore we aimed to develop sex-specific diagnostic models to enable the early identification of men and women at high-risk of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with or without symptoms of heart failure who require more aggressive preventative strategies.
Design: Individual patient data from four primary care heart failure-screening studies were analysed (1371 participants, excluding patients classified as heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction <50%).
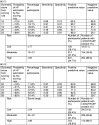
Methods: Eleven candidate predictors were entered into logistic regression models to be associated with the presence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction/heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in men and women separately. Internal-external cross-validation was performed to develop and validate the models.
Results: Increased age and β-blocker therapy remained as predictors in both the models for men and women. The model for men additionally consisted of increased body mass index, moderate to severe shortness of breath, increased pulse pressure and history of ischaemic heart disease. The models performed moderately and similarly well in men (c-statistics range 0.60-0.75) and women (c-statistics range 0.51-0.76) and the performance improved significantly following the addition of N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (c-statistics range 0.61-0.80 in women and 0.68-0.80 in men).
Conclusions: We provide an easy-to-use screening tool for use in the community, which can improve the early detection of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction/heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in high-risk men and women and optimise tailoring of preventive interventions.
Keywords: Screening; community; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; sex.
Figures

Comment in
-
Community screening for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019 Apr;26(6):611-612. doi: 10.1177/2047487319828177. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30722679 No abstract available.
-
Cutting the Gordian knot of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: Role of opportunistic screening models.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019 Oct;26(15):1666-1669. doi: 10.1177/2047487319865049. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31319716 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cui X, Zhou J, Jin X, et al. Prevalence and correlates of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in elderly community residents. Int J Cardiol 2016; 227: 1–6. - PubMed
-
- Aurigemma GP, Gottdiener JS, Shemanski L, et al. Predictive value of systolic and diastolic function for incident congestive heart failure in the elderly: The cardiovascular health study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 37: 1042–1048. - PubMed
-
- Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Burnett JC, et al. Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: Appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. Intern Med 2003; 289: 194–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

