Aidi Injection, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Injection, Could Be Used as an Adjuvant Drug to Improve Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis
- PMID: 30482065
- PMCID: PMC6432675
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735418810799
Aidi Injection, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Injection, Could Be Used as an Adjuvant Drug to Improve Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Abstract
Background: Clinical research has paid increasing attention to quality of life (QoL) in recent years, but the assessment of QoL is difficult, hampered by the subjectivity, complexity, and adherence of patients and physicians. According to previous studies, QoL in cancer patients is related to performance status (PS) and influenced by chemotherapy-related toxicity. Aidi injection, a traditional Chinese medicine injection, is used as an adjuvant drug to enhance effectiveness of chemotherapy. The study aims to investigate whether Aidi injection could improve QoL by improving PS and reducing toxicity caused by chemotherapy.
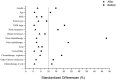
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed at the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medicine University. Data of consecutive patients diagnosed with cancers between January 2014 and June 2017 were retrieved from the electronic medical record system. After a 1:1 propensity score match, patients were then divided into 2 groups based on the therapies used, that is, Aidi injection combined with chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone, and the PS, chemotherapy-related toxicity, and combined medication information were compared. The effect of different dosages of Aidi injection on patients was further explored.
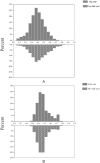
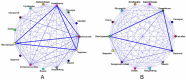
Results: A total of 3200 patients were included in this study. Aidi injection combined with chemotherapy exhibited significantly benefit in PS ( P < .001, odds ratio [OR] 3.4, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.4-4.8) compared with chemotherapy alone after adjusting for the factors that affect PS. The improvement rate of PS in the Aidi group was significantly higher than in the control group across the stratification of gender, age, tumor type, TNM stage, body mass index, nodal metastasis, prior chemotherapy, chemotherapy regimens, other Chinese tradition medicines, and chemotherapy cycle. Meanwhile, Aidi injection used synchronously with chemotherapeutic drugs could decrease the incident rate of damage to liver and kidney function, myelosuppression, and gastrointestinal reactions caused by chemotherapy.
Conclusion: It was indicated that the integrative approach combining chemotherapy with Aidi injection, especially with the conventional dosage of Aidi injection, had significant benefit on QoL in cancer patients.
Keywords: Aidi injection; ECOG score; chemotherapy-related toxicity; performance status; propensity score match; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of Aidi injection plus paclitaxel-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of 31 randomized controlled trials following the PRISMA guidelines.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jan 10;228:110-122. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.024. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30243827
-
The Hepatorenal Toxicity and Tumor Response of Chemotherapy With or Without Aidi Injection in Advanced Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 80 Randomized Controlled Trials.Clin Ther. 2020 Mar;42(3):515-543.e31. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.01.011. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32088021
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of aidi injection combination with vinorelbine and cisplatin for advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 54 randomized controlled trials.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar;153:104637. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104637. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 31935454
-
Assessment on the Efficacy and Safety of Aidi Injection Combined with Vinorelbine and Cisplatin for Treatment of Advanced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Mar 20;129(6):723-30. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.178016. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 26960377 Free PMC article.
-
Can Aidi injection restore cellular immunity and improve clinical efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy? A meta-analysis of 17 randomized controlled trials following the PRISMA guidelines.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Nov;95(44):e5210. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005210. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27858864 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Meta-Analysis of Aidi Injection and First-Generation Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Treating Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2021 Jan-Dec;26:2515690X211010733. doi: 10.1177/2515690X211010733. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 33926244 Free PMC article.
-
Aidi injection reduces doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting carbonyl reductase 1 expression.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1616-1624. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2110127. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35980105 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxysafflor yellow A induces autophagy in human liver cancer cells by regulating Beclin 1 and ERK expression.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Apr;19(4):2989-2996. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8552. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32256785 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic herb-drug interactions between Aidi injection and doxorubicin in rats with diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Sep 6;22(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00515-9. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34488896 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine with Western Medicine on Endometrial Carcinoma and Its Influence on Ultrasound, MRI, Tumor Markers HE4 and CA125.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 2;2021:6053406. doi: 10.1155/2021/6053406. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34899952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeong WS, Jun M, Kong AN. Nrf2: a potential molecular target for cancer chemoprevention by natural compounds. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8:99-106. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:48-58. - PubMed
-
- Lv C, Shi C, Li L, Wen X, Xian CJ. Chinese herbal medicines in the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2018;12:174-180. - PubMed
-
- Ling CQ, Yue XQ, Ling C. Three advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine to prevent and treat tumor. J Integr Med. 2014;12:331-335. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources