The biochemistry of early meiotic recombination intermediates
- PMID: 30482074
- PMCID: PMC6300103
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1553355
The biochemistry of early meiotic recombination intermediates
Abstract
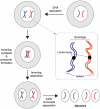
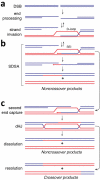
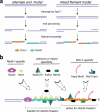
Meiosis is the basis for sexual reproduction and is marked by the sequential reduction of chromosome number during successive cell cycles, resulting in four haploid gametes. A central component of the meiotic program is the formation and repair of programmed double strand breaks. Recombination-driven repair of these meiotic breaks differs from recombination during mitosis in that meiotic breaks are preferentially repaired using the homologous chromosomes in a process known as homolog bias. Homolog bias allows for physical interactions between homologous chromosomes that are required for proper chromosome segregation, and the formation of crossover products ensuring genetic diversity in progeny. An important aspect of meiosis in the differential regulation of the two eukaryotic RecA homologs, Rad51 and Dmc1. In this review we will discuss the relationship between biological programs designed to regulate recombinase function.
Keywords: Homologous recombination; dmc1; meiosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367271 Free PMC article.
-
A mutant form of Dmc1 that bypasses the requirement for accessory protein Mei5-Sae3 reveals independent activities of Mei5-Sae3 and Rad51 in Dmc1 filament stability.PLoS Genet. 2019 Dec 2;15(12):e1008217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008217. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31790385 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of Rad51 activity during meiosis in yeast prevents competition with Dmc1 for repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1004005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004005. Epub 2014 Jan 23. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24465215 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of RecA homologues Rad51 and Dmc1 during meiotic recombination.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;107(3-4):201-7. doi: 10.1159/000080598. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15467365 Review.
-
From meiosis to postmeiotic events: uncovering the molecular roles of the meiosis-specific recombinase Dmc1.FEBS J. 2010 Feb;277(3):590-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07503.x. Epub 2009 Dec 15. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20015079 Review.
Cited by
-
PLK1 depletion alters homologous recombination and synaptonemal complex disassembly events during mammalian spermatogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 May 1;33(5):ar37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-03-0115. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35274968 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of fidelity-governing factors in human recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 from cryo-EM structures.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 14;12(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20258-1. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33446654 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of end resection pathways for double-strand break regions containing ribonucleotides and base lesions.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 18;11(1):3088. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16903-4. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32555206 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel System for the Detection of Spontaneous Abortion-Causing Aneuploidy and Its Erroneous Chromosome Origins through the Combination of Low-Pass Copy Number Variation Sequencing and NGS-Based STR Tests.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):1809. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051809. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902595 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis HOP2 gene has a role in preventing illegitimate connections between nonhomologous chromosome regions.Chromosome Res. 2022 Mar;30(1):59-75. doi: 10.1007/s10577-021-09681-2. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Chromosome Res. 2022. PMID: 35064347
References
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
