Chi-miR-3031 regulates beta-casein via the PI3K/AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs)
- PMID: 30482199
- PMCID: PMC6258393
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-018-1695-6
Chi-miR-3031 regulates beta-casein via the PI3K/AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs)
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs can regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level through translational repression or target degradation. Our previous investigations examined the differential expression levels of chi-miR-3031 in caprine mammary gland tissues in colostrum and common milk stages.
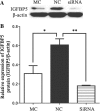
Results: The present study detected the role of chi-miR-3031 in the lactation mechanisms of GMECs. High-throughput sequencing was used to analyze transcriptomic landscapes of GMECs transfected with chi-miR-3031 mimics (MC) and a mimic negative control (NC). In the MC and NC groups, we acquired 39,793,503 and 36,531,517 uniquely mapped reads, respectively, accounting for 85.85 and 81.66% of total reads. In the MC group, 180 differentially expressed unigenes were downregulated, whereas 157 unigenes were upregulated. KEGG pathway analyses showed that the prolactin, TNF and ErbB signaling pathways, including TGFα, PIK3R3, IGF2, ELF5, IGFBP5 and LHβ genes, played important roles in mammary development and milk secretion. Results from transcriptome sequencing, real-time PCR and western blotting showed that chi-miR-3031 suppressed the expression of IGFBP5 mRNA and protein. The expression levels of β-casein significantly increased in the MC and siRNA-IGFBP5 groups. We observed that the down-regulation of IGFBP5 activated mTOR at the Ser2448 site in GMECs transfected with MC and siRNA-IGFBP5. Previous findings and our results showed that chi-miR-3031 activated the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and increased β-casein expression by down-regulating IGFBP5.
Conclusions: These findings will afford valuable information for improving milk quality and contribute the development of potential methods for amending lactation performance.
Keywords: Dairy goats; Gene expression; Milk components; Transcriptome; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal care and procedures were performed in accordance with institutional and national guidelines and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Northwest A&F University (China).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Huppertz, T. 2013. Chemistry of the caseins. Pages 135–160 in Advanced dairy chemistry. Vol. 1A: Proteins: Basic Aspects. 4th ed. P. L. H. McSweeney and P. F. Fox, ed. Springer Science+Business Media, New York, NY.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31601925/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016T90954 and 2014M552498/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2015KTCQ03-08 and 2016KTZDNY02-04/Shaanxi Science and Technology Innovation Project Plan
- 2013BSJJ003/PhD Research Funding of Northwest A&F University
- 2452015029/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

