Role of TLR4-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway in LPS-induced pulmonary epithelial hyperpermeability
- PMID: 30482200
- PMCID: PMC6258407
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-018-0735-0
Role of TLR4-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway in LPS-induced pulmonary epithelial hyperpermeability
Abstract
Background: The breakdown of alveolar barrier dysfunction contributes to Lipopolysaccharide stimulated pulmonary edema and acute lung injury. Actin cytoskeleton has been implicated to be critical in regulation of epithelial barrier. Here, we performed in vivo and in vitro study to investigate role of TLR4-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway in LPS-induced ALI.
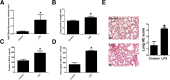
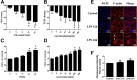
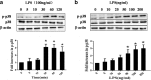
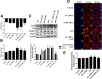
Methods: For in vivo studies, 6-8-week-old C57 mice were used, Bronchoalveolar lavage Fluid /Blood fluorescent ratio, wet-to-dry lung weight ratio, as well as protein concentrations and neutrophil cell counts in BALF were detected as either directly or indirectly indicators of pulmonary alveolar barrier dysfunction. And hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed to estimate pulmonary injury. The in vitro explorations of transepithelial permeability were achieved through transepithelial electrical resistance measurement and testing of FITC-Dextran transepithelial flux in A549. In addition, cytoskeletal rearrangement was tested through F-actin immunostaining. And SB203580 was used to inhibit p38 MAPK activation, while siRNA was administered to genetically knockdown specific protein.
Results: We showed that LPS triggered activation of p38 MAPK, rearrangement of cytoskeleton which resulted in severe epithelial hyperpermeability and lung edema. A549 pretreated with TLR4 siRNA、p38 MAPK siRNA and its inhibitor SB203580 displayed a lower permeability and fewer stress fibers formation after LPS stimulation, accompanied with lower phosphorylation level of p38 MAPK and Hsp27, which verified the involvement of TLR4-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 in LPS-evoked alveolar epithelial injury. Inhibition of p38 MAPK activity with SB203580 in vivo attenuated pulmonary edema formation and hyperpermeability in response to LPS.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that LPS increased alveolar epithelial permeability both in vitro and in vivo and that TLR4- p38 MAPK- Hsp27 signal pathway dependent actin remolding was involved in this process.
Keywords: ALI; Alveolar barrier dysfunction; Cytoskeletal rearrangement; Hsp27; LPS; P38 MAPK; TLR4.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Animal Care Committee of the Southern Medical University of China.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase up-regulates LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in the development of lung injury and RAW 264.7 macrophages.Toxicology. 2006 Aug 1;225(1):36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.04.053. Epub 2006 May 9. Toxicology. 2006. PMID: 16793190
-
Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits angiotensin II-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction via inhibition of the p38 MAPK/HSP27 pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Oct;31(10):1401-6. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.75. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20644550 Free PMC article.
-
HSP27 phosphorylation protects against endothelial barrier dysfunction under burn serum challenge.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 31;463(3):377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.152. Epub 2015 May 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26028560
-
Regulators of endothelial and epithelial barrier integrity and function in acute lung injury.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 15;77(12):1763-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.01.014. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19428331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in acute lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;47(4):395-404. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0100TR. Epub 2012 May 31. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22652197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of normalisation and error model choice on the distribution of the maximum likelihood estimator for a biochemical reaction.IET Syst Biol. 2023 Feb;17(1):1-13. doi: 10.1049/syb2.12055. Epub 2022 Nov 28. IET Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 36440585 Free PMC article.
-
CCL25 Inhibition Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Inflammation.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 25;15:3309-3321. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S352544. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35782530 Free PMC article.
-
SPAK-p38 MAPK signal pathway modulates claudin-18 and barrier function of alveolar epithelium after hyperoxic exposure.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Feb 15;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01408-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 33588817 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Dysfunction of the Intestinal Barrier in the Pathogenesis of Complications of Acute Poisoning.J Evol Biochem Physiol. 2022;58(4):1075-1098. doi: 10.1134/S0022093022040123. Epub 2022 Aug 28. J Evol Biochem Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36061072 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 is one of the receptors for Chikungunya virus envelope protein E2 and regulates virus induced pro-inflammatory responses in host macrophages.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1139808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139808. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153546 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

