Sodium channel TRPM4 and sodium/calcium exchangers (NCX) cooperate in the control of Ca2+-induced mucin secretion from goblet cells
- PMID: 30482841
- PMCID: PMC6341386
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000848
Sodium channel TRPM4 and sodium/calcium exchangers (NCX) cooperate in the control of Ca2+-induced mucin secretion from goblet cells
Abstract
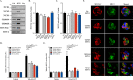
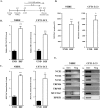
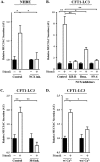
Regulated mucin secretion is essential for the formation of the mucus layer that protects the underlying epithelial cells from foreign particles. Alterations in the quantity or quality of secreted mucins are therefore detrimental to airway and colon physiology. Based on various biochemical assays in several human cell lines, we report here that Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 2 (NCX2) works in conjunction with transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 (TRPM4), and perhaps TRPM5, Na+ channels to control Ca2+-mediated secretion of both mucin 2 (MUC2) and MUC5AC from HT29-18N2 colonic cancer cells. Differentiated normal bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells and tracheal cells from patients with cystic fibrosis (CFT1-LC3) expressed only TRPM4 and all three isoforms of NCXs. Blocking the activity of TRPM4 or NCX proteins abrogated MUC5AC secretion from NHBE and CFT1-LC3 cells. Altogether, our findings reveal that NCX and TRPM4/TRPM5 are both required for mucin secretion. We therefore propose that these two proteins could be potential pharmacological targets to control mucus-related pathologies such as cystic fibrosis.
Keywords: MUC2; MUC5AC; TRPM4; TRPM5; cystic fibrosis; goblet cell; mucin; secretion; sodium-calcium exchange; transient receptor potential channels (TRP channels).
© 2019 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

