The recombination mediator proteins RecFOR maintain RecA* levels for maximal DNA polymerase V Mut activity
- PMID: 30482842
- PMCID: PMC6341379
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005726
The recombination mediator proteins RecFOR maintain RecA* levels for maximal DNA polymerase V Mut activity
Abstract
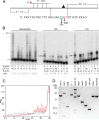
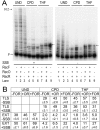
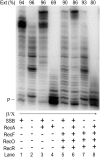
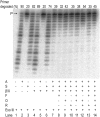
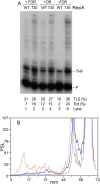
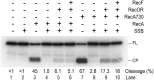
DNA template damage can potentially block DNA replication. Cells have therefore developed different strategies to repair template lesions. Activation of the bacterial lesion bypass DNA polymerase V (Pol V) requires both the cleavage of the UmuD subunit to UmuD' and the acquisition of a monomer of activated RecA recombinase, forming Pol V Mut. Both of these events are mediated by the generation of RecA* via the formation of a RecA-ssDNA filament during the SOS response. Formation of RecA* is itself modulated by competition with the ssDNA-binding protein (SSB) for binding to ssDNA. Previous observations have demonstrated that RecA filament formation on SSB-coated DNA can be favored in the presence of the recombination mediator proteins RecF, RecO, and RecR. We show here using purified proteins that in the presence of SSB and RecA, a stable RecA-ssDNA filament is not formed, although sufficient RecA* is generated to support some activation of Pol V. The presence of RecFOR increased RecA* generation and allowed Pol V to synthesize longer DNA products and to elongate from an unpaired primer terminus opposite template damage, also without the generation of a stable RecA-ssDNA filament.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA polymerase; DNA recombination; DNA repair; RecA; lesion bypass; nucleic acid enzymology; recombination mediator protein; translesion synthesis.
© 2019 Raychaudhury and Marians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

