Inhibition of MERTK Promotes Suppression of Tumor Growth in BRAF Mutant and BRAF Wild-Type Melanoma
- PMID: 30482852
- PMCID: PMC9787186
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0456
Inhibition of MERTK Promotes Suppression of Tumor Growth in BRAF Mutant and BRAF Wild-Type Melanoma
Abstract
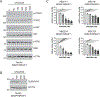
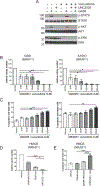
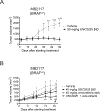
Molecularly-targeted agents have improved outcomes for a subset of patients with BRAF-mutated melanoma, but treatment of resistant and BRAF wild-type tumors remains a challenge. The MERTK receptor tyrosine kinase is aberrantly expressed in melanoma and can contribute to oncogenic phenotypes. Here we report the effect of treatment with a MERTK-selective small molecule inhibitor, UNC2025, in preclinical models of melanoma. In melanoma cell lines, treatment with UNC2025 potently inhibited phosphorylation of MERTK and downstream signaling, induced cell death, and decreased colony formation. In patient-derived melanoma xenograft models, treatment with UNC2025 blocked or significantly reduced tumor growth. Importantly, UNC2025 had similar biochemical and functional effects in both BRAF-mutated and BRAF wild-type models and irrespective of NRAS mutational status, implicating MERTK inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy in tumors that are not amenable to BRAF-targeting and for which there are limited treatment options. In BRAF-mutated cell lines, combined treatment with UNC2025 and the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib provided effective inhibition of oncogenic signaling through ERK, AKT, and STAT6, increased induction of cell death, and decreased colony-forming potential. Similarly, in NRAS-mutated cell lines, addition of UNC2025 to cobimetinib therapy increased cell death and decreased colony-forming potential. In a BRAF-mutated patient-derived xenograft, treatment with combined UNC2025 and vemurafenib was well-tolerated and significantly decreased tumor growth compared with vemurafenib alone. These data support the use of UNC2025 for treatment of melanoma, irrespective of BRAF or NRAS mutational status, and suggest a role for MERTK and targeted combination therapy in BRAF and NRAS-mutated melanoma.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

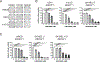
References
-
- Wellbrock C, Ogilvie L, Hedley D, Karasarides M, Martin J, Niculescu-Duvaz D, et al. V599EB-RAF is an oncogene in melanocytes. Cancer Res. 2004;64(7):2338–42. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Choi JW, Kim YS. Frequencies of BRAF and NRAS mutations are different in histological types and sites of origin of cutaneous melanoma: a meta-analysis. The British journal of dermatology. 2011;164(4):776–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

