A Successfully Treated Case of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma with Exacerbation of Dermatomyositis
- PMID: 30483040
- PMCID: PMC6244101
- DOI: 10.1159/000493185
A Successfully Treated Case of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma with Exacerbation of Dermatomyositis
Abstract
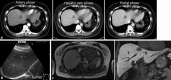
Dermatomyositis (DM) is often found in conjunction with malignant tumors such as lung, cervical, and breast cancer. However, the association with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is extremely rare. Moreover, to our knowledge, there have been no previous reports of DM discovered because of exacerbation of DM. Our case was a 44-year-old female with dry cough, myalgia, and arthralgia. We performed hepatic resection for intrahepatic ICC. She was diagnosed with DM, and combination treatment with prednisolone and tacrolimus was started. During outpatient visits, her symptoms worsened, and she was hospitalized due to deterioration of her primary disease. On detailed examination, a malignant lesion in the liver was discovered. After operation, the symptoms of DM remain stable by taking prednisolone and tacrolimus. The patient was suspected to have paraneoplastic syndrome, which was discovered due to the exacerbation of the DM that was caused by the intrahepatic ICC.
Keywords: Dermatomyositis; Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Paraneoplastic syndrome.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dermatomyositis with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and data mining based on machine learning.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 18;13:1206043. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1206043. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37664040 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbation of Dermatomyositis with Recurrence of Rectal Cancer: A Case Report.Case Rep Oncol. 2015 Nov 10;8(3):482-6. doi: 10.1159/000439519. eCollection 2015 Sep-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26668568 Free PMC article.
-
Successful resection of liver metastasis detected by exacerbation of skin symptom in a patient with dermatomyositis accompanied by rectal cancer: a case report and literature review.Surg Case Rep. 2017 Dec;3(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40792-016-0281-z. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Surg Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28054279 Free PMC article.
-
Primary or metastatic hepatic carcinoma? A breast cancer patient after adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy postoperatively with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and review of the literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Jul 15;14(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0943-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27422708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double primary hepatic cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) originating from hepatic progenitor cell: a case report and review of the literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Aug 17;14(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0974-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27535234 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dermatomyositis with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and data mining based on machine learning.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 18;13:1206043. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1206043. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37664040 Free PMC article.
-
Paraneoplastic syndromes in cholangiocarcinoma.World J Hepatol. 2020 Nov 27;12(11):897-907. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.897. World J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33312417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dalakas MC, Hohlfeld R. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 2003 Sep;362((9388)):971–82. - PubMed
-
- Hill CL, Zhang Y, Sigurgeirsson B, Pukkala E, Mellemkjaer L, Airio A, et al. Frequency of specific cancer types in dermatomyositis and polymyositis: a population-based study. Lancet. 2001 Jan;357((9250)):96–100. - PubMed
-
- Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelöf B, Edhag O, Allander E. Risk of cancer in patients with dermatomyositis or polymyositis. A population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1992 Feb;326((6)):363–7. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BE, Mawr B. Dermatomyositis and malignancy. A review of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Jan;84((1)):68–76. - PubMed
-
- Requena C, Alfaro A, Traves V, Nagore E, Llombart B, Serra C, et al. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis: a study of 12 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014 Sep;105((7)):675–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

