A Rare Cause of Dysphagia and Weight Loss
- PMID: 30483043
- PMCID: PMC6244109
- DOI: 10.1159/000493919
A Rare Cause of Dysphagia and Weight Loss
Abstract
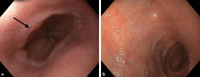
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is a rare connective tissue disorder with clinical features that overlap with systemic lupus erythematous, systemic sclerosis, and polymyositis. We report the case of a patient who presented with dysphagia, 25-lb weight loss, difficulty opening her mouth, and joint pain. Dysphagia workup showed a normal barium swallow and normal-appearing EGD but esophageal manometry consistent with severe dysmotility. Through further laboratory and imaging studies, the patient met the diagnostic criteria for MCTD. She had marked improvement in her dysphagia with steroids, biologic therapy, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
Keywords: Esophageal dysmotility; High-resolution esophageal manometry; Mixed connective tissue disease.
Figures


References
-
- Gunnarsson R, Molberg O, Gilboe IM, Gran JT, PAHNOR1 Study Group The prevalence and incidence of mixed connective tissue disease: a national multicentre survey of Norwegian patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jun;70((6)):1047–51. - PubMed
-
- Schneider HA, Yonker RA, Longley S, Katz P, Mathias J, Panush RS. Scleroderma esophagus: a nonspecific entity. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100((6)):848–50. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JB, Kretschmar JM, Gerhardt DC, Winship DH, Winn D, Treadwell EL, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestations of mixed connective tissue disease. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98((5 Pt 1)):1232–8. - PubMed
-
- Ling TC, Johnston BT. Esophageal investigations in connective tissue disease: which tests are most appropriate? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001 Jan;32((1)):33–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

