MicroRNA-210-5p Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Early Vascular Dementia Rat Model Through Targeting Snap25
- PMID: 30483048
- PMCID: PMC6243094
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00388
MicroRNA-210-5p Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Early Vascular Dementia Rat Model Through Targeting Snap25
Abstract
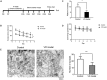
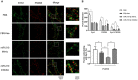
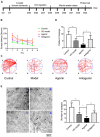
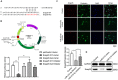
Vascular dementia (VD) is the most common form of dementia in elderly people. However, little is understood about the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) involved in cognitive impairment in early VD. Here, a VD model induced by chronic cerebral ischemia and fetal bovine serum (FBS)-free cell model that detects synapse formation was established to investigate the function of miRNAs in early VD. The microarray analysis and real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed that miR-210-5p increased significantly in the hippocampus of rats with 4 weeks of ischemia. The VD model rats also displayed significant cognitive deficits and synaptic loss. The overexpression of miR-210-5p decreased the synaptic number in primary hippocampal neurons, whereas specific suppression of miR-210-5p resulted in the formation of more synapses. Additionally, intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of miR-210-5p agomir to VD rats aggravated phenotypes of cognitive impairment and synaptic loss. These VD-induced phenotypes were effectively attenuated by miR-210-5p antagomir. Moreover, bioinformatic prediction revealed that synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 KDa (Snap25) mRNA is targeted by miR-210-5p. The miR-210-5p decreased the luciferase activities of 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of Snap25 mRNA. Mutation of predicted miR-210-5p binding sites in the 3' UTR of Snap25 mRNA abolished the miR-210-5p-induced decrease in luciferase activity. Western blot and immunofluorescence staining confirmed that miR-210-5p targets Snap25. Finally, RT-quantitative PCR (qPCR) and immunofluorescence staining detected that miR-210-5p agomir downregulated Snap25 expression in the cornu ammonis1 (CA1) region of hippocampi in VD rats, whereas miR-210-5p antagomir upregulated Snap25 expression. Altogether, miR-210-5p contributes to cognitive impairment in chronic ischemia-induced VD model through the regulation of Snap25 expression, which potentially provides an opportunity to develop a new therapeutic strategy for VD.
Keywords: Snap25; cognitive impairment; miR-210-5p; synaptic loss; vascular dementia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-181b-5p attenuates early postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice.Cytokine. 2019 Aug;120:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 31003188
-
miR‑134‑5p/Foxp2/Syn1 is involved in cognitive impairment in an early vascular dementia rat model.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Nov;44(5):1729-1740. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4331. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31545395 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-153 impairs presynaptic plasticity by blocking vesicle release following chronic brain hypoperfusion.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 6;18(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00551-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32252776 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA alterations in neuropathologic cognitive disorders with an emphasis on dementia: Lessons from animal models.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Feb;236(2):806-823. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29908. Epub 2020 Jun 30. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32602584 Review.
-
Atherosclerosis: The Culprit and Co-victim of Vascular Dementia.Front Neurosci. 2021 Aug 6;15:673440. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.673440. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34421513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Dysregulation in the Hippocampus of Rats with Noise-Induced Hearing Loss.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Sep 6;2021:1377195. doi: 10.1155/2021/1377195. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34527169 Free PMC article.
-
Increased intestinal bile acid absorption contributes to age-related cognitive impairment.Cell Rep Med. 2024 May 21;5(5):101543. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101543. Epub 2024 May 1. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 38697101 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA-330-5p induces manic-like behaviors in REM sleep-deprived rats by enhancing tyrosine hydroxylase expression.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jun;29(6):1525-1536. doi: 10.1111/cns.14121. Epub 2023 Feb 16. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 36794530 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Deficiency of MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Confers Resistance to Neuropathological Damage and Cognitive Dysfunction in Experimental Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Jun;9(17):e2104986. doi: 10.1002/advs.202104986. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35403823 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy promotes sorafenib resistance through hypoxia-inducible ATAD3A dependent Axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 7;39(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01768-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33280610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aski M. L., Rezvani M. E., Khaksari M., Hafizi Z., Pirmoradi Z., Niknazar S., et al. . (2018). Neuroprotective effect of berberine chloride on cognitive impairment and hippocampal damage in experimental model of vascular dementia. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 21, 53–58. 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.23195.5865 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

