Web-Based Interfaces for Virtual C. elegans Neuron Model Definition, Network Configuration, Behavioral Experiment Definition and Experiment Results Visualization
- PMID: 30483089
- PMCID: PMC6243129
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2018.00080
Web-Based Interfaces for Virtual C. elegans Neuron Model Definition, Network Configuration, Behavioral Experiment Definition and Experiment Results Visualization
Abstract
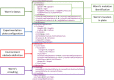
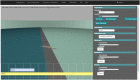
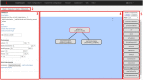
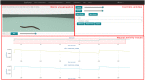
The Si elegans platform targets the complete virtualization of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, and its environment. This paper presents a suite of unified web-based Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) as the main user interaction point, and discusses their underlying technologies and methods. The user-friendly features of this tool suite enable users to graphically create neuron and network models, and behavioral experiments, without requiring knowledge of domain-specific computer-science tools. The framework furthermore allows the graphical visualization of all simulation results using a worm locomotion and neural activity viewer. Models, experiment definitions and results can be exported in a machine-readable format, thereby facilitating reproducible and cross-platform execution of in silico C. elegans experiments in other simulation environments. This is made possible by a novel XML-based behavioral experiment definition encoding format, a NeuroML XML-based model generation and network configuration description language, and their associated GUIs. User survey data confirms the platform usability and functionality, and provides insights into future directions for web-based simulation GUIs of C. elegans and other living organisms. The tool suite is available online to the scientific community and its source code has been made available.
Keywords: C. elegans experiment definition and results visualization; NeuroML; behavioral experiment input encoding; biological neural networks; brain-inspired computation; in silico simulation; low entropy model specification (LEMS); neuronal activity visualization.
Figures









References
-
- Abbott L., Kepler T. B. (1990). Model neurons: from hodgkin-huxley to hopfield, in Statistical Mechanics of Neural Networks, ed Garrido L. (Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer; ), 5–18.
-
- Allard J., Cotin S., Faure F., Bensoussan P.-J., Poyer F., Duriez C., et al. (2007). Sofa-an open source framework for medical simulation, in MMVR 15-Medicine Meets Virtual Reality, Vol. 125, eds Westwood D., Haluck R. S., Hoffman H. M., Mogel G. T., Phillips R., Robb R. A., Vosburgh K. G. (Amsterdam: IOP Press; ), 13–18. - PubMed
-
- Altun Z., Hall D. (2002). Wormatlas. Available online at: http://www.wormatlas.org (Accessed 31 January, 2018).
-
- Bhatla N. (2018). Wormweb.org - C. elegans Interactive Neural Network. Available online at: http://wormweb.org/neuralnet#c=bag&m=1 (Accessed 31 January, 2018).
-
- Blau A., Callaly F., Cawley S., Coffey A., De Mauro A., Epelde G., et al. (2014). The si elegans project – the challenges and prospects of emulating caenorhabditis elegans, in Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems eds Duff A., Lepora N. F., Mura A., Prescott T. J., Verschure P. F. M. J. (Cham: Springer International Publishing; ), 436–438.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

