Iris Morphological Features in Patients with 360° Angle-Closure Neovascular Glaucoma: An Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Study
- PMID: 30483110
- PMCID: PMC6244033
- DOI: 10.1159/000493418
Iris Morphological Features in Patients with 360° Angle-Closure Neovascular Glaucoma: An Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography Study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate iris morphological features in 360° angle-closure neovascular glaucoma (NVG) by swept-source anterior segment optical coherence tomography (ASOCT).
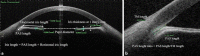
Patients and methods: In this retrospective, clinic-based, comparative study, 14 patients with 360° angle-closure NVG and 14 healthy age-matched control subjects were enrolled. All patients enrolled had no prior glaucoma surgery but underwent cataract surgery with intraocular lens implantation. Horizontal scanning images of swept-source ASOCT were analyzed using software calipers in temporal and nasal angle areas. The iris thickness at 1 and 2 mm from the pupil edge, iris length, trabecular meshwork length, peripheral anterior synechia (PAS) length, PAS height ratio (PAS length/trabecular meshwork length), and pupil diameter were measured.
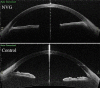
Results: Between the groups, there were no statistically significant differences in iris length, trabecular meshwork length, and pupil diameter (p > 0.05). However, the iris thickness was significantly reduced in the NVG group compared with the control group in the temporal and nasal areas (0.306 vs. 0.563 mm/0.326 vs. 0.645 mm at 1 mm, 0.278 vs. 0.523 mm/0.282 vs. 0.546 mm at 2 mm, respectively) (mean, all p < 0.001). In the NVG group, PAS height ratios were 1.55 ± 0.45 (mean ± standard deviation) (range, 0.58-2.30) and 1.55 ± 0.78 (range, 0.68-3.68) at the temporal and nasal angles, respectively.
Conclusions: In patients with 360° angle-closure NVG, the iris thickness decreased to about 50% of that in healthy subjects, and the PAS length exceeded the trabecular meshwork length by about 1.5 times.
Keywords: Angle closure; Anterior segment optical coherence tomography; Neovascular glaucoma; Peripheral anterior synechia.
Figures
References
-
- Fernández-Vigo JI, García-Feijóo J, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, García-Bella J, Fernández-Vigo JA. Morphometry of the trabecular meshwork in vivo in a healthy population using fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Feb;56((3)):1782–8. - PubMed
-
- Usui T, Tomidokoro A, Mishima K, Mataki N, Mayama C, Honda N, et al. Identification of Schlemm's canal and its surrounding tissues by anterior segment fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Sep;52((9)):6934–9. - PubMed
-
- Invernizzi A, Giardini P, Cigada M, Viola F, Staurenghi G. Three-dimensional morphometric analysis of the iris by swept-source anterior segment optical coherence tomography in a Caucasian population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jul;56((8)):4796–801. - PubMed
-
- Nongpiur ME, Aboobakar IF, Baskaran M, Narayanaswamy A, Sakata LM, Wu R, et al. Association of baseline anterior segment parameters with the development of incident gonioscopic angle closure. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Mar;135((3)):252–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

