Pentraxins and Fc Receptor-Mediated Immune Responses
- PMID: 30483265
- PMCID: PMC6243083
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02607
Pentraxins and Fc Receptor-Mediated Immune Responses
Abstract
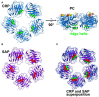
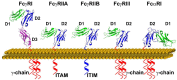
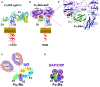
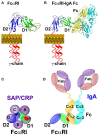
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. These proteins are highly conserved over the course of evolution being present as far back as 250 million years ago. Mammalian pentraxins are characterized by the presence of five identical non-covalently linked subunits. Each subunit has a structurally conserved site for calcium-dependent ligand binding. The biological activities of the pentraxins established over many years include the ability to mediate opsonization for phagocytosis and complement activation. Pentraxins have an important role in protection from infection from pathogenic bacteria, and regulation of the inflammatory response. It was recognized early on that some of these functions are mediated by activation of the classical complement pathway through C1q. However, experimental evidence suggested that cellular receptors for pentraxins also play a role in phagocytosis. More recent experimental evidence indicates a direct link between pentraxins and Fc receptors. The Fc receptors were first identified as the major receptors for immunoglobulins. The avidity of the interaction between IgG complexes and Fc receptors is greatly enhanced when multivalent ligands interact with the IgG binding sites and activation of signaling pathways requires Fc receptor crosslinking. Human pentraxins bind and activate human and mouse IgG receptors, FcγRI and FcγRII, and the human IgA receptor, FcαRI. The affinities of the interactions between Fc receptors and pentraxins in solution and on cell surfaces are similar to antibody binding to low affinity Fc receptors. Crystallographic and mutagenesis studies have defined the structural features of these interactions and determined the stoichiometry of binding as one-to-one. Pentraxin aggregation or binding to multivalent ligands increases the avidity of binding and results in activation of these receptors for phagocytosis and cytokine synthesis. This review will discuss the structural and functional characteristics of pentraxin Fc receptor interactions and their implications for host defense and inflammation.
Keywords: CRP; Fc receptor activation by pentraxin; SAP; pentraxin; structure and function.
Figures
References
-
- Alles VV, Bottazzi B, Peri G, Golay J, Introna M, Mantovani A. Inducible expression of PTX3, a new member of the pentraxin family, in human mononuclear phagocytes. Blood (1994) 84:3483–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

