Function and Regulation of Human Terminal Uridylyltransferases
- PMID: 30483311
- PMCID: PMC6240794
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00538
Function and Regulation of Human Terminal Uridylyltransferases
Abstract
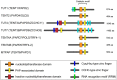
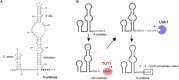
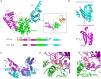
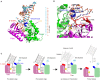
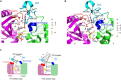
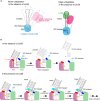
RNA uridylylation plays a pivotal role in the biogenesis and metabolism of functional RNAs, and regulates cellular gene expression. RNA uridylylation is catalyzed by a subset of proteins from the non-canonical terminal nucleotidyltransferase family. In human, three proteins (TUT1, TUT4, and TUT7) have been shown to exhibit template-independent uridylylation activity at 3'-end of specific RNAs. TUT1 catalyzes oligo-uridylylation of U6 small nuclear (sn) RNA, which catalyzes mRNA splicing. Oligo-uridylylation of U6 snRNA is required for U6 snRNA maturation, U4/U6-di-snRNP formation, and U6 snRNA recycling during mRNA splicing. TUT4 and TUT7 catalyze mono- or oligo-uridylylation of precursor let-7 (pre-let-7). Let-7 RNA is broadly expressed in somatic cells and regulates cellular proliferation and differentiation. Mono-uridylylation of pre-let-7 by TUT4/7 promotes subsequent Dicer processing to up-regulate let-7 biogenesis. Oligo-uridylylation of pre-let-7 by TUT4/7 is dependent on an RNA-binding protein, Lin28. Oligo-uridylylated pre-let-7 is less responsive to processing by Dicer and degraded by an exonuclease DIS3L2. As a result, let-7 expression is repressed. Uridylylation of pre-let-7 depends on the context of the 3'-region of pre-let-7 and cell type. In this review, we focus on the 3' uridylylation of U6 snRNA and pre-let-7, and describe the current understanding of mechanism of activity and regulation of human TUT1 and TUT4/7, based on their crystal structures that have been recently solved.
Keywords: TUT1; TUT4/7; TUTase; U6 snRNA; biogenesis; let-7; splicing; terminal uridylyltransferase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structure of human TUT1:U6 snRNA complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1314. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1314. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39831302 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of U6 snRNA-specific terminal uridylyltransferase.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 7;8:15788. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15788. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28589955 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the Lin28-interacting module of human terminal uridylyltransferase that regulates let-7 expression.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 29;10(1):1960. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09966-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31036859 Free PMC article.
-
3' RNA Uridylation in Epitranscriptomics, Gene Regulation, and Disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jul 13;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00061. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30057901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
U6 RNA biogenesis and disease association.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Sep-Oct;4(5):581-92. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1181. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23776162 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA modifications: importance in immune cell biology and related diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Sep 22;7(1):334. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01175-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36138023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of human TUT1:U6 snRNA complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1314. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1314. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39831302 Free PMC article.
-
AGO-bound mature miRNAs are oligouridylated by TUTs and subsequently degraded by DIS3L2.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 2;11(1):2765. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16533-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32488030 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of U6 snRNA oligouridylation by human TUT1.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 10;14(1):4686. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40420-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37563152 Free PMC article.
-
Target-directed microRNA degradation: Mechanisms, significance, and functional implications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Mar-Apr;15(2):e1832. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1832. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38448799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

