Effects of assisted oocyte activation with calcium- ionophore and strontium chloride on in vitro ICSI outcomes
- PMID: 30483383
- PMCID: PMC6251390
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.30422.7331
Effects of assisted oocyte activation with calcium- ionophore and strontium chloride on in vitro ICSI outcomes
Abstract
Objectives: Failed fertilization after intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is mainly attributed to failed oocyte activation and can be overcome by artificial oocyte activation (AOA). The present study aims to compare in vitro outcomes of ICSI following two different assisted oocyte activation chemical procedures (SrCl2 and Ionomycin) in sibling oocytes of ICSI candidates.
Materials and methods: From March 2015 until February 2016, 105 infertile men with 99-100% abnormal sperm morphology, irrespective of sperm motility, concentration, or origin (semen or testicular) were included in this study. Out of these, 66 couples accepted to be included in the study group (Ionomycin/ SrCl2) and 39 couples requested routine AOA procedure (Ionomycin) as external control group. Primary outcomes of this study (fertilization, embryo quality, and post-implantation development) were compared between these groups.
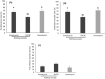
Results: Significantly higher oocyte activation (67.90±3.6% vs. 51.16±3.6%, P=0.004) and fertilization (65.23±3.63% vs. 49.65±3.63%, P=0.008) rates were observed in sibling oocytes treated with Ionomycin in comparison to the SrCl2 sibling group. Percentage of top quality embryos was insignificantly higher in SrCl2 groups compared to the Ionomycin group (29.90±4.27 vs. 20.65±4.05%, P=0.26).
Conclusion: Ionomycin may be superior to SrCl2 for inducing oocyte activation. However, SrCl2 may be a more efficient means to support the development of better quality embryos following ICSI.
Keywords: Fertilization; Implantation; Ionomycin; Pregnancy; Strontium.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose and all authors support submission to this journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of pre- and post-implantation development following the application of three artificial activating stimuli in a mouse model with round-headed sperm cells deficient for oocyte activation.Hum Reprod. 2013 May;28(5):1190-8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det038. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23482335
-
Successful pregnancy after SrCl2 oocyte activation in couples with repeated low fertilization rates following calcium ionophore treatment.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2014 Jun;60(3):177-82. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2014.900832. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2014. PMID: 24645921
-
Artificial oocyte activation with SrCl2 or calcimycin after ICSI improves clinical and embryological outcomes compared with ICSI alone: results of a randomized clinical trial.Hum Reprod. 2018 Sep 1;33(9):1636-1644. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey258. Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 30099496 Clinical Trial.
-
Artificial oocyte activation: physiological, pathophysiological and ethical aspects.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Feb;65(1):3-11. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1516000. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30207496 Review.
-
The present status of artificial oocyte activation in assisted reproductive technology.Reprod Med Biol. 2008 Aug 3;7(3):133-142. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0578.2008.00210.x. eCollection 2008 Sep. Reprod Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 29699294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oocyte activation deficiency and assisted oocyte activation: mechanisms, obstacles and prospects for clinical application.Hum Reprod Open. 2022 Feb 7;2022(2):hoac003. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoac003. eCollection 2022. Hum Reprod Open. 2022. PMID: 35261925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Role of Sperm-Specific PLC-Zeta in Egg Activation and Male Factor Infertility: An Update.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jan 29;8:28. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00028. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32064262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Ionophore (A23187) Rescues the Activation of Unfertilized Oocytes After Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection and Chromosome Analysis of Blastocyst After Activation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 15;12:692082. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.692082. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34335469 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Male Infertility-Related Fertilization Failure.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 1;9(12):3899. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123899. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33271815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assisted Oocyte Activation following Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection: A Sensible Option for Infertile Couples with Severe Teratozoospermia.Int J Fertil Steril. 2023 Feb 1;17(2):92-98. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2023.1973580.1395. Int J Fertil Steril. 2023. PMID: 36906825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palermo GD, Neri QV, Takeuchi T, Rosenwaks Z. ICSI: where we have been and where we are going. Semin Reprod Med. 2009;27:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Mahutte NG, Arici A. Failed fertilization: is it predictable? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2003;15:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Javed M, Esfandiari N, Casper RF. Failed fertilization after clinical intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Reprod Biomed Online. 2010;20:56–67. - PubMed
-
- Swain JE, Pool TB. ART failure: oocyte contributions to unsuccessful fertilization. Hum Reprod Update. 2008;14:431–1446. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
