Interaction of aquaporin 4 and N-methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor 1 in traumatic brain injury of rats
- PMID: 30483388
- PMCID: PMC6251393
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29135.7037
Interaction of aquaporin 4 and N-methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor 1 in traumatic brain injury of rats
Abstract
Objectives: methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor (NMDAR) and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) are involved in the molecular cascade of edema after traumatic brain injury (TBI) and are potential targets of studies in pharmacology and medicine. However, their association and interactions are still unknown.
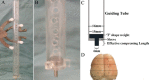
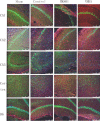
Materials and methods: We established a rat TBI model in this study. The cellular distribution patterns of AQP4 after inhibition of NMDAR were determined by Western blotting and immunoreactive staining. Furthermore, the regulation of NMDA receptor 1 by AQP4 was studied by injection of a viral vector targeting AQP4 by RNAi into the rat brain before TBI.
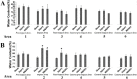
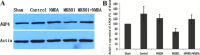
Results: The results suggest that AQP4 protein expression increased significantly (P<0.05) after TBI and was down-regulated by the NMDAR inhibitor MK801. This decrease could be partly reversed using the NMDAR agonist NMDA. This indicated that AQP4 mRNA levels and protein expression are regulated by the NMDA signaling pathway. By injection of AQP4 RNAi viral vector into the brain of TBI rat models, we found that the mRNA and protein levels of NMDAR decreased significantly (P<0.05). This suggested that NMDAR is also regulated by AQP4.
Conclusion: These data suggested that the inhibition of AQP4 down-regulates NMDAR expression, which might be one of the mechanisms involved in edema after TBI.
Keywords: Aquaporin 4; Edema; N-methyl-D-aspartate NMDA receptor; NMDAR1; Traumatic brain injury.
Figures
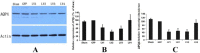
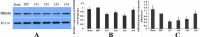
Similar articles
-
Aquaporin 4 in Traumatic Brain Injury: From Molecular Pathways to Therapeutic Target.Neurochem Res. 2022 Apr;47(4):860-871. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03512-w. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35088218 Review.
-
Temporal alterations in aquaporin and transcription factor HIF1α expression following penetrating ballistic-like brain injury (PBBI).Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014 May;60:81-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24769105
-
Neuroprotective effects of lentivirus-mediated aquaporin-4 gene silencing in rat model of traumatic brain injury.Neurol Res. 2022 Aug;44(8):692-699. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2022.2039509. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Neurol Res. 2022. PMID: 35189787
-
[Effect of silencing aquaporin 4 on learning and memory dysfunction in rats with traumatic brain injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Feb;30(2):170-175. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.02.015. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29402369 Chinese.
-
AQP4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) coexisting with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis: A case report and literature review.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Oct;35:185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Jul 20. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 31398657 Review.
Cited by
-
Perceiving traumatic brain injury from glymphatic system.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 31. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03126-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40745390 Review.
-
Inhibition of NMDA Receptors Downregulates Astrocytic AQP4 to Suppress Seizures.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Nov;40(8):1283-1295. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00813-6. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32107753 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental study of cerebral edema and expression of VEGF and AQP4 in the penumbra area of rat brain trauma.Sci Rep. 2025 May 16;15(1):17040. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02071-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40379765 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin 4 in Traumatic Brain Injury: From Molecular Pathways to Therapeutic Target.Neurochem Res. 2022 Apr;47(4):860-871. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03512-w. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35088218 Review.
References
-
- Schouten JW. Neuroprotection in traumatic brain injury: a complex struggle against the biology of nature. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2007;13:134–142. - PubMed
-
- McIntosh TK, Vink R, Soares H, Hayes R, Simon R. Effect of noncompetitive blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on the neurochemical sequelae of experimental brain injury. J Neurochem. 1990;55:1170–1179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
