Generation of motor neurons from human amygdala-derived neural stem-like cells
- PMID: 30483389
- PMCID: PMC6251401
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29587.7146
Generation of motor neurons from human amygdala-derived neural stem-like cells
Abstract
Objectives: Among several cell sources, adult human neural stem/progenitor cells (hNS/PCs) have been considered outstanding cells for performing mechanistic studies in in vitro and in vivo models of neurological disorders as well as for potential utility in cell-based therapeutic approaches. Previous studies addressed the isolation and culture of hNS/PCs from human neocortical and hippocampal tissues. However, little data are available on hNS/PCs obtained from the adult human amygdala.
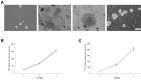
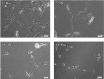
Materials and methods: The present study explored the capacity of the amygdala harvested from resected brain tissues of patients with medically refractory epilepsy to generate neurosphere-like bodies and motor neuron-like cells.
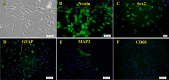
Results: Although the proliferation process was slow, a considerable amount of cells was obtained after the 3rd passage. In addition, the cells could generate motor neuron-like cells under appropriate culture conditions.
Conclusion: Isolation and culture of these cells enable us to improve our knowledge of the role of the amygdala in some neurological and psychological disorders and provide a novel source for therapeutic cell transplantation.
Keywords: Brain; Hippocampus; Intractable Epilepsy; Motor neuron; Neural stem cells.
Figures


References
-
- Kennea NL, Mehmet H. Neural stem cells. J Pathol. 2002;197:536–550. - PubMed
-
- Vescovi AL, Parati EA, Gritti A, Poulin P, Ferrario M, Wanke E, Frölichsthal-Schoeller P, Cova L, Arcellana-Panlilio M, Colombo A, Galli R. Isolation and cloning of multipotential stem cells from the embryonic human CNS and establishment of transplantable human neural stem cell lines by epigenetic stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1999;156:71–83. - PubMed
-
- Pollard SM, Conti L, Sun Y, Goffredo D, Smith A. Adherent neural stem (NS) cells from fetal and adult forebrain. Cereb Cortex. 2006;16 (Suppl 1):i112–120. - PubMed
-
- McLaren A. Ethical and social considerations of stem cell research. Nature. 2001;414:129–131. - PubMed
-
- Delcroix GJ, Schiller PC, Benoit JP, Montero-Menei CN. Adult cell therapy for brain neuronal damages and the role of tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31:2105–2120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
