A Wor1-Like Transcription Factor Is Essential for Virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 30483479
- PMCID: PMC6243373
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00369
A Wor1-Like Transcription Factor Is Essential for Virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
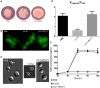
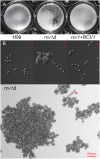
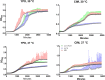
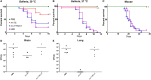
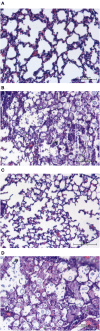
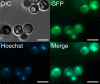
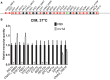
Gti1/Pac2 transcription factors occur exclusively in fungi and their roles vary according to species, including regulating morphological transition and virulence, mating and secondary metabolism. Many of these functions are important for fungal pathogenesis. We therefore hypothesized that one of the two proteins of this family in Cryptococcus neoformans, a major pathogen of humans, would also control virulence-associated cellular processes. Elimination of this protein in C. neoformans results in reduced polysaccharide capsule expression and defective cytokinesis and growth at 37°C. The mutant loses virulence in a mouse model of cryptococcal infection and retains only partial virulence in the Galleria mellonella alternative model at 30°C. We performed RNA-Seq experiments on the mutant and found abolished transcription of genes that, in combination, are known to account for all the observed phenotypes. The protein has been named Required for cytokinesis and virulence 1 (Rcv1).
Keywords: Cryptococcus neoformans; capsule; cytokinesis; transcription factor; virulence.
Figures

References
-
- Caspari T. (1997). Onset of gluconate-H+ symport in Schizosaccharomyces pombe is regulated by the kinases Wis1 and Pka1, and requires the gti1+ gene product. J. Cell Sci. 110(Pt 20), 2599–2608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

