Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection
- PMID: 30483519
- PMCID: PMC6244293
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2018.11.654
Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection
Abstract
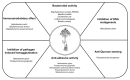
Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) is a well-known traditional herbal medicine that plays a protective role against microbial attack. Several studies have revealed its anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and immune-modulatory effects. Ginseng contains several components that vary according to the year of cultivation and the processing method used, such as heating, drying, and steaming, which induce different degrees of pharmacological activities. This review discusses the antibacterial effects of ginseng against pathogenic bacterial infections. We describe how ginseng regulates pathogenic factors that are harmful to the host and discuss the therapeutic potential of ginseng as a natural antibacterial drug to combat bacterial infectious disease, which is a global public health challenge. The components of ginseng could be novel alternatives to solve the growing problem of antibiotic resistance and toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lee OR, Sathiyaraj G, Kim YJ, In JG, Kwon WS, Kim JH, Yang DC. Defense Genes Induced by Pathogens and Abiotic Stresses in Panax Ginseng C. A. Meyer. J Ginseng Res. 2011;35(1):1–11. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2011.35.1.001. - DOI
-
- Helmes S. Cancer Prevention and Therapeutics: Panax Ginseng. Altern Med Rev. 2004;9(3):259–275. - PubMed
-
- Radad K, Gille G, Liu L, Rausch WD. Use of Ginseng in Medicine With Emphasis on Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100(3):175–186. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
