Risk stratifying the screening of Barrett's esophagus: An Asian perspective
- PMID: 30483537
- PMCID: PMC6207036
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12013
Risk stratifying the screening of Barrett's esophagus: An Asian perspective
Abstract
Background and aim: Barrett's esophagus (BE) is a premalignant condition for esophageal adenocarcinoma. Although risk factors exist for screening patients in the West, we aimed to determine the factors in terms of demographics and symptoms for patients in an Asian setting.
Methods: We recruited 1378 patients over a 7-year period as part of an ongoing gastric cancer screening program. An appropriately designed questionnaire was utilized to determine the necessary risk factors and symptoms with endoscopic analysis and subsequent histological confirmation as the gold standard. We utilized the existence of intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus as the primary diagnostic pathology.
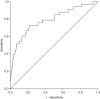
Results: We demonstrated that no symptoms were indicative of BE in an Asian setting. Age (odds ratio 1.081, 95% confidence interval 1.022-1.143) and male gender (odds ratio 4.808, 95% confidence interval 1.727-13.33) proved significant demographic factors for the presence of intestinal metaplasia (P 0.007, 0.003, respectively).
Conclusions: We advocate the utilization of increasing age and male gender as the primary risk factors for patients at risk of BE. We also recommend astute examination of the distal esophagus whilst patients undergo simultaneous gastric cancer screening.
Keywords: Barrett's esophagus; gastroesophageal reflux disease; intestinal metaplasia; risk factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Barrett's esophagus and intestinal metaplasia of gastric cardia: prevalence, clinical, endoscopic and histological features.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2014 Mar;23(1):19-25. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2014. PMID: 24689092
-
Short segment Barrett's esophagus and distal gastric intestinal metaplasia.Arq Gastroenterol. 2006 Apr-Jun;43(2):117-20. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032006000200011. Arq Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17119666
-
[Specialized intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus in gastroesophageal reflux disease: prevalence and clinico-demographic features].Arq Gastroenterol. 2003 Oct-Dec;40(4):220-6. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032003000400005. Epub 2004 May 31. Arq Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 15264043 Portuguese.
-
The diagnosis and management of Barrett's esophagus.Adv Surg. 1999;33:29-68. Adv Surg. 1999. PMID: 10572561 Review.
-
Management of Barrett's esophagus free of dysplasia.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997 Jul;9(3):279-84. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997. PMID: 9263346 Review.
References
-
- Hvid‐Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM et al Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett's esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011; 365: 1375–83. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald RC, di Pietro M, Ragunath K et al British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2014; 63: 7–42. - PubMed
-
- Lee JWJ, Koh C, Lim LG et al Tu1296 prospective cohort study of gastric intestinal metaplasia progression and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2006; 150: S867–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources