Quantitative analysis of opioids and cannabinoids in wastewater samples
- PMID: 30483615
- PMCID: PMC6197101
- DOI: 10.1080/20961790.2016.1270812
Quantitative analysis of opioids and cannabinoids in wastewater samples
Abstract
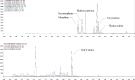
Wastewater-based epidemiology is an innovative approach that uses the analysis of human excretion products in wastewater to obtain information about exposure to drugs in defined population groups. We developed and validated an analytical method for the simultaneous determination of opioids (morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, oxymorphone and hydromorphone), and cannabinoids (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, 11-nor-9-carboxy-tetrahydrocannabinol (THCCOOH) and THCCOOH-glucuronide) in raw-influent wastewater samples by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Method validation included linearity (5-1 000 ng/L for opioids, 10-1 000 ng/L for cannabinoids), imprecision (<21.2%), accuracy (83%-131%), matrix effect (from -35.1% to -14.7%) and extraction efficiency (25%-84%), limit of detection (1-5 ng/L) and quantification (5-10 ng/L) and auto-sampler stability (no loss detected). River and wastewater samples were collected in triplicate from different locations in New York City and stored at -20 °C until analysis. Water from sewage overflow location tested positive for morphine (10.7 ng/L), oxycodone (4.2-23.5 ng/L), oxymorphone (4.8 ng/L) and hydromorphone (4.2 ng/L). Raw influent wastewater samples tested positive for morphine (133.0-258.3 ng/L), oxycodone (31.1-63.6 ng/L), oxymorphone (16.0-56.8 ng/L), hydromorphone (6.8-18.0 ng/L), hydrocodone (4.0-12.8 ng/L) and THCCOOH (168.2-772.0 ng/L). This method is sensitive and specific for opioids and marijuana determination in wastewater samples.
Keywords: Forensic science; cannabis; chromatography liquid; forensic toxicology; opioid; solid phase extraction; tandem mass spectrometry; wastewater.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wastewater analysis for nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines, opioids and cannabis in New York City.Forensic Sci Res. 2019 May 31;4(2):152-167. doi: 10.1080/20961790.2019.1609388. eCollection 2019. Forensic Sci Res. 2019. PMID: 31304444 Free PMC article.
-
A fully automated approach for the analysis of 37 psychoactive substances in raw wastewater based on on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2018 Nov 16;1576:80-89. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2018.09.038. Epub 2018 Sep 18. J Chromatogr A. 2018. PMID: 30292522
-
Simultaneous analysis of opioid analgesics and their metabolites in municipal wastewaters and river water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2018 Jan 19;1533:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.12.025. Epub 2017 Dec 11. J Chromatogr A. 2018. PMID: 29274731
-
Forensic drug testing for opiates. VI. Urine testing for hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxymorphone, and oxycodone with commercial opiate immunoassays and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.J Anal Toxicol. 1995 Jan-Feb;19(1):18-26. doi: 10.1093/jat/19.1.18. J Anal Toxicol. 1995. PMID: 7536861 Clinical Trial.
-
Simultaneous ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of amphetamine and amphetamine-like stimulants, cocaine and its metabolites, and a cannabis metabolite in surface water and urban wastewater.J Chromatogr A. 2009 Apr 10;1216(15):3078-89. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.067. Epub 2009 Jan 29. J Chromatogr A. 2009. PMID: 19201418
Cited by
-
The use of fast molecular descriptors and artificial neural networks approach in organochlorine compounds electron ionization mass spectra classification.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Sep;26(27):28188-28201. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05968-4. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31363975 Free PMC article.
-
Wastewater analysis for nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines, opioids and cannabis in New York City.Forensic Sci Res. 2019 May 31;4(2):152-167. doi: 10.1080/20961790.2019.1609388. eCollection 2019. Forensic Sci Res. 2019. PMID: 31304444 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of 39 drugs and metabolites, including 8 glucuronide conjugates, in an upstream wastewater network via HPLC-MS/MS.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021 Jun 30;1176:122747. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.122747. Epub 2021 May 13. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34052556 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, Multianalyte Detection of Opioid Metabolites in Wastewater.ACS Nano. 2022 Mar 22;16(3):3704-3714. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c07094. Epub 2022 Feb 24. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 35201755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castiglioni S, Thomas KV, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, et al. . Testing wastewater to detect illicit drugs: state of the art, potential and research needs. Sci Total Environ. 2014;487:613–620. - PubMed
-
- Daughton CG. Illicit Drugs: contaminants in the environment and utility in forensic epidemiology. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2011;210:59–110. Whitcare D.M.(ed.). - PubMed
-
- Daghir E, Markuszewski MJ. Disposition of Drugs of abuse and their metabolites in wastewater as a method of the estimation of Drug consumption. Curr Drug Metab. 2010;11:629–638. - PubMed
-
- European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) [Internet] Wastewater analysis and drugs: a European multi-city study. [cited2015. Nov 11]. Available from: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/topics/pods/waste-water-analysis
-
- Subedi B, Kannan K. Occurrence and fate of select psychoactive pharmaceuticals and antihypertensives in two wastewater treatment plants in New York State, USA. Sci Total Environ. 2015;514:273–280. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

