State of the art in post-mortem forensic imaging in China
- PMID: 30483623
- PMCID: PMC6197115
- DOI: 10.1080/20961790.2017.1337501
State of the art in post-mortem forensic imaging in China
Abstract
The autopsy and histopathologic examination are traditional and classic approaches in forensic pathology. In recent years, with the tremendous progresses of computer technology and medical imaging technology, the developed post-mortem computer tomography, post-mortem magnetic resonance imaging and other new methods provide non-invasive, intuitive, high-precision examining methods and research tools for the forensic pathology. As a result, the reconstruction of the injury as well as the analysis of injury mechanism has been essentially achieved. Such methods have become popular in the research field of forensic science and related work has also been carried out in China. This paper reviews the development and application of abovementioned post-mortem forensic imaging methods in China based on the relevant literature.
Keywords: Forensic science; finite element analysis; post-mortem computer tomography; post-mortem computer tomography angiography; post-mortem forensic imaging; post-mortem magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures
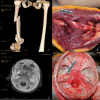
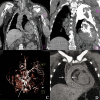


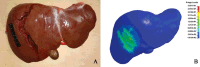
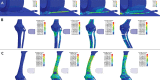
Similar articles
-
[Forensic radiology : Introduction and overview].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024 Nov;64(11):823-829. doi: 10.1007/s00117-024-01365-2. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39240319 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Evolution of post-mortem coronary imaging: from selective coronary arteriography to post-mortem CT-angiography and beyond.Radiol Med. 2018 May;123(5):351-358. doi: 10.1007/s11547-018-0855-x. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Radiol Med. 2018. PMID: 29357039 Review.
-
State-of-the-art of visualization in post-mortem imaging.APMIS. 2012 Apr;120(4):316-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2011.02857.x. APMIS. 2012. PMID: 22429214 Review.
-
Application of contrast media in post-mortem imaging (CT and MRI).Radiol Med. 2015 Sep;120(9):824-34. doi: 10.1007/s11547-015-0532-2. Epub 2015 Apr 5. Radiol Med. 2015. PMID: 25841652 Review.
-
Microbiology in minimally invasive autopsy: best techniques to detect infection. ESGFOR (ESCMID study group of forensic and post-mortem microbiology) guidelines.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2021 Mar;17(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s12024-020-00337-x. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33464531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Virtual, 3D Multimodal Approach to Victim and Crime Scene Reconstruction.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;13(17):2764. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13172764. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of drowning using postmortem computed tomography combined with endoscopic autopsy: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e19182. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019182. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176043 Free PMC article.
-
Application of postmortem computed tomography angiography to settle a medical dispute after aortic dissection surgery: a forensic case report.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023 Aug 18;18(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02353-8. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37596679 Free PMC article.
-
Forensic imaging: a powerful tool in modern forensic investigation.Forensic Sci Res. 2022 Mar 7;7(3):385-392. doi: 10.1080/20961790.2021.2008705. eCollection 2022. Forensic Sci Res. 2022. PMID: 36353311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autopsy diagnosis of acupuncture-induced bilateral tension pneumothorax using whole-body postmortem computed tomography: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e13059. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013059. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Press C, Approach TV. The virtopsy approach. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2009.
-
- Dirnhofer R, Jackowski C, Vock P, et al. . VIRTOPSY: minimally invasive, imaging-guided virtual autopsy. RadioGraphics 2006;26:1305–1333. - PubMed
-
- Thali M. Virtual autopsy (virtopsy) in forensic science: from the scalpel to the scanner. Der Pathologe. 2011;32:292–295. Epub 2011/11/09. - PubMed
-
- Liu N, Yang S, Zhao H, et al. . Application of multi-slice computed tomography in biomechanical analysis of traffic accidents. Fa yi xue za zhi. 2010;26:401–405, 12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

