Functional role of RBM10 in lung adenocarcinoma proliferation
- PMID: 30483773
- PMCID: PMC6317669
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4643
Functional role of RBM10 in lung adenocarcinoma proliferation
Abstract
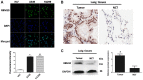
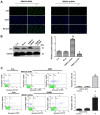
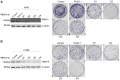
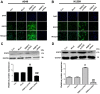
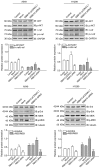
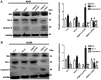
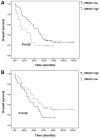
Lung cancer is one of the most common causes of morbidity and mortality among malignant tumors worldwide. The poor prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinomas is primarily due to its strong ability to invade and metastasize. Recent research has indicated that RNA‑binding protein 10 (RBM10) is mutated in lung adenocarcinoma, and is closely associated with tumor proliferation and apoptosis; however, the precise role of RBM10 in lung adenocarcinoma remains unclear. Our preliminary experiments (unpublished data) revealed that RBM10 expression was upregulated in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and tissues. In this study, we first detected the protein expression level of RBM10 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and tissues, and we then examined the effects of RBM10 overexpression and downregulation (via small interfering RNA) on the proliferation and apoptosis of stable lung adenocarcinoma cells, along with its possible mechanisms of action. We also used clinical samples of lung adenocarcinomas to verify our results. We found that RBM10 protein was overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma cells and tissues, and it reduced p53 expression (as detected by immunofluorescence assay and western blot analysis) in A549 cells and inhibited apoptosis (as shown by flow cytometric assay). RBM10 also promoted cell growth and proliferation in vitro and increased cell migration in a cell wound scratch assay. Furthermore, we found that RBM10 activated key proliferative signaling pathways [such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphoinositide 3‑kinase (PI3K)‑AKT pathways] and inhibited apoptotic pathways. In addition, we demonstrated that a high expression of RBM10 protein in patient tissue samples was associated with a shorter overall survival time and a poor prognosis. On the whole, the findings of this study indicate that RBM10 may function as an oncogene in lung cancer, and may thus prove to be a novel therapeutic target for the prophylaxis and treatment of lung adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma; RNA-binding protein 10; proliferation; apoptosis.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

