Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome‑wide gene expression profiling analysis
- PMID: 30483789
- PMCID: PMC6297798
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9677
Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome‑wide gene expression profiling analysis
Abstract
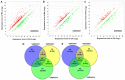
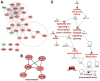
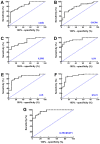
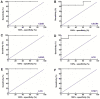
The present study aimed to identify potential novel biomarkers in synovial tissue obtained from patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Osteoarthritis (OA) for differential diagnosis. The genome‑wide expression profiling datasets of synovial tissues from RA and OA cohorts, including GSE55235, GSE55457 and GSE55584 datasets, were retrieved and used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs; P<0.05; false discovery rate <0.05 and Fold Change >2) between RA and OA using R software. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses of DEGs were performed to determine molecular and biochemical pathways associated with the identified DEGs, and a protein‑protein interaction (PPI) network of the DEGs was constructed using Cytoscape software. Significant modules in the PPI network and candidate driver genes were screened using the Molecular Complex Detection Algorithm. Potential biomarkers were evaluated by receiver operating characteristic and logistic regression analyses. Large numbers of DEGs were detected, including 273, 205 and 179 DEGs in the GSE55235, GSE55457 and GSE55584 datasets, respectively. Among them, 80 DEGs exhibited identical expression trends in all the three datasets, including 49 upregulated and 31 downregulated genes in patients with RA. DEGs in patients suffering from RA compared with patients suffering from OA were predominantly associated with the primary immunodeficiency pathway, including interleukin 7 receptor (IL7R) and signal transducer activator of transcription 1 (STAT1). The sensitivity of IL7R + STAT1 to differentiate RA from OA was 93.94% with a specificity of 80.77%. The results generated from analyses of the GSE36700 dataset were closely associated with results generated from analyses of GSE55235, GSE55457 and GSE55584 datasets, which further verified the reliability of the aforementioned results. The results of the present study suggested that increased expression of IL7R and STAT1 in synovial tissue as well as in the primary immunodeficiency may be associated with RA occurrence. These identified novel biomarkers may be used to predict disease occurrence and clinically differentiate RA from OA.
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis; osteoarthritis; pathway; protein-protein interaction; sensitivity; specificity.
Figures
References
-
- García-Bermúdez M, López-Mejías R, González-Juanatey C, Castañeda S, Miranda-Filloy JA, Blanco R, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Balsa A, González-Alvaro I, Gómez-Vaquero C, et al. Lack of association between TLR4 rs4986790 polymorphism and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. DNA Cell Biol. 2012;31:1214–1220. doi: 10.1089/dna.2011.1582. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

